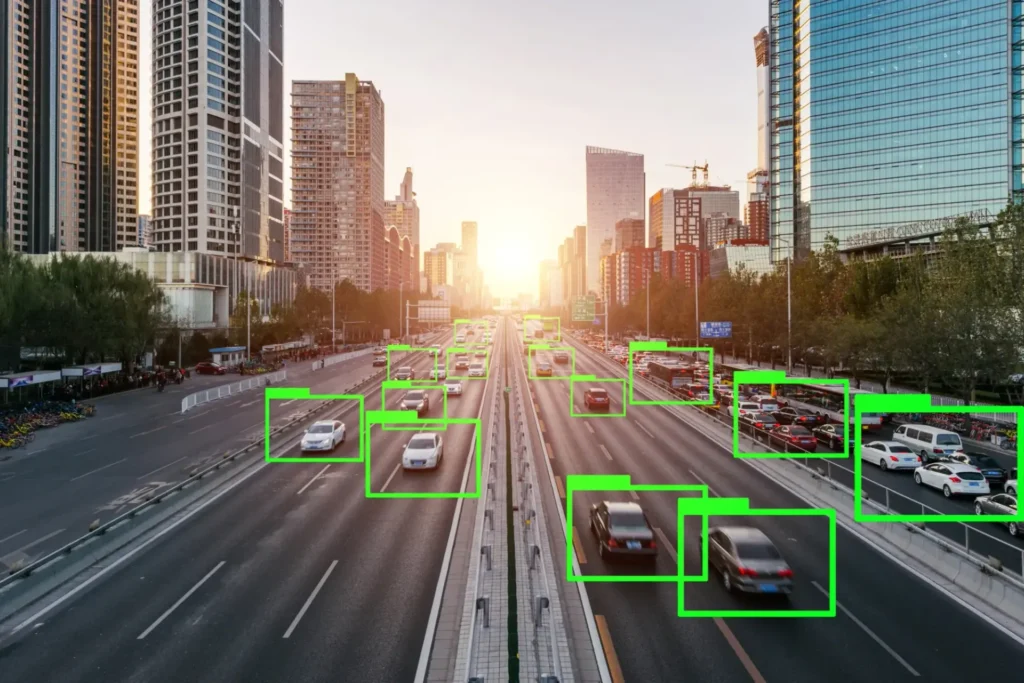
Introduction to keypoint annotation – what it is and where it is used
Keypoint annotation for hand gesture recognition
Think about modern sports broadcasts that highlight a player’s movement, calculate running speed, or predict their next move. Or the way mobile apps let you control actions with just your hands-like showing a thumbs-up to pause music. These capabilities are not magic. They are powered by Computer Vision, and at the center of it lies a crucial technique called Keypoint Annotation.
To train AI models to detect movements, recognize faces, interpret gestures, or track objects, datasets must be accurately labeled using keypoints-precise locations on an object or body that act as anchors for machine interpretation. In this article, we explain what keypoint annotation is, how it works in large-scale AI projects, the challenges involved, and the industries that rely on it.

What is Keypoint Annotation?
Keypoint annotation is a data labeling method used to mark specific, meaningful points within an image or video. These points are often joints, landmarks, or structural references that machine learning models use to understand shapes, orientation, or movement.
Visualize it as placing “digital pins” on important coordinates—like marking the elbows, knees, and shoulders on a human body, or mapping eyes, nose, and mouth on a face. Once these points are connected, they form a skeleton or wireframe, allowing AI to interpret motion, posture, or facial expressions.
This approach isn’t limited to humans. It can also be used to:
- Track paw and limb positions of animals in veterinary research
- Mark corners of machinery components in industrial automation
- Identify finger joints for gesture-based interfaces
- Detect damage or deformation in manufacturing inspection tasks
The strength of keypoint annotation lies in its ability to convert unstructured pixels into structured motion data, enabling AI to reason not just about what is in an image—but how it behaves.
How Keypoint Annotation Works
The annotation process typically follows these stages:
- Dataset Upload
Images or video frames are uploaded to an annotation platform such as Coral Mountain. - Skeleton / Keypoint Schema Definition
A layout of keypoints is defined—for example, 17 keypoints for full human body pose, or 68 keypoints for facial mapping. Each keypoint is given a label and a relationship (which point connects to which). - Annotation Phase
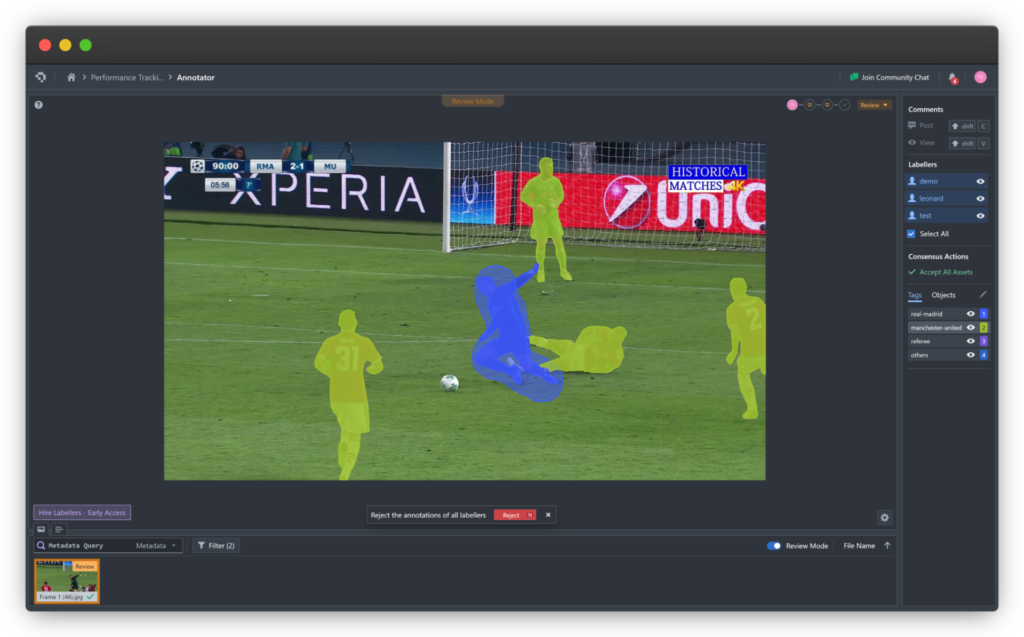
Annotators manually drag and place keypoints at the correct locations across frames. In complex videos, interpolation tools help by automatically predicting keypoint positions between frames. - Review and Quality Control
Multiple annotators or supervisors review the data to fix misplacements, enforce consistency, and maintain accuracy across large datasets. - Export for Training AI Models
The final structured data is exported into formats like JSON, COCO, or CSV to be used for machine learning pipelines.
Coral Mountain’s platform supports AI-assisted placement, auto-tracking, and keyframe propagation, which significantly reduces annotation fatigue while improving precision at scale.
Challenges in Keypoint Annotation
Although keypoint annotation delivers powerful training data, it comes with several difficulties:
- High Manual Effort
Placing dozens of keypoints across thousands of images or video frames is slow work. Even with automation, annotators must verify every position to prevent small errors from disrupting learning outcomes.
- Variation and Ambiguity
Not all visual data is clean. Poor lighting, occlusion, motion blur, or overlapping objects often force annotators to make judgment calls—leading to inconsistencies if no clear guidelines exist.
- Human Error Accumulation
Even a one-pixel misplacement across repeated frames can degrade model performance. Without strict verification systems, bad data silently propagates downstream.
- Privacy and Compliance Risks
When annotating faces, medical scans, or surveillance footage, it is essential to handle sensitive information securely, anonymize identities when needed, and comply with regulatory frameworks (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.).
- Real-world Consequences of Inaccuracy
Incorrect keypoints in self-driving cars or healthcare applications can lead to harmful predictions. Therefore, accuracy is not just a metric—it’s a safety requirement.
Best Practices for Keypoint Annotation
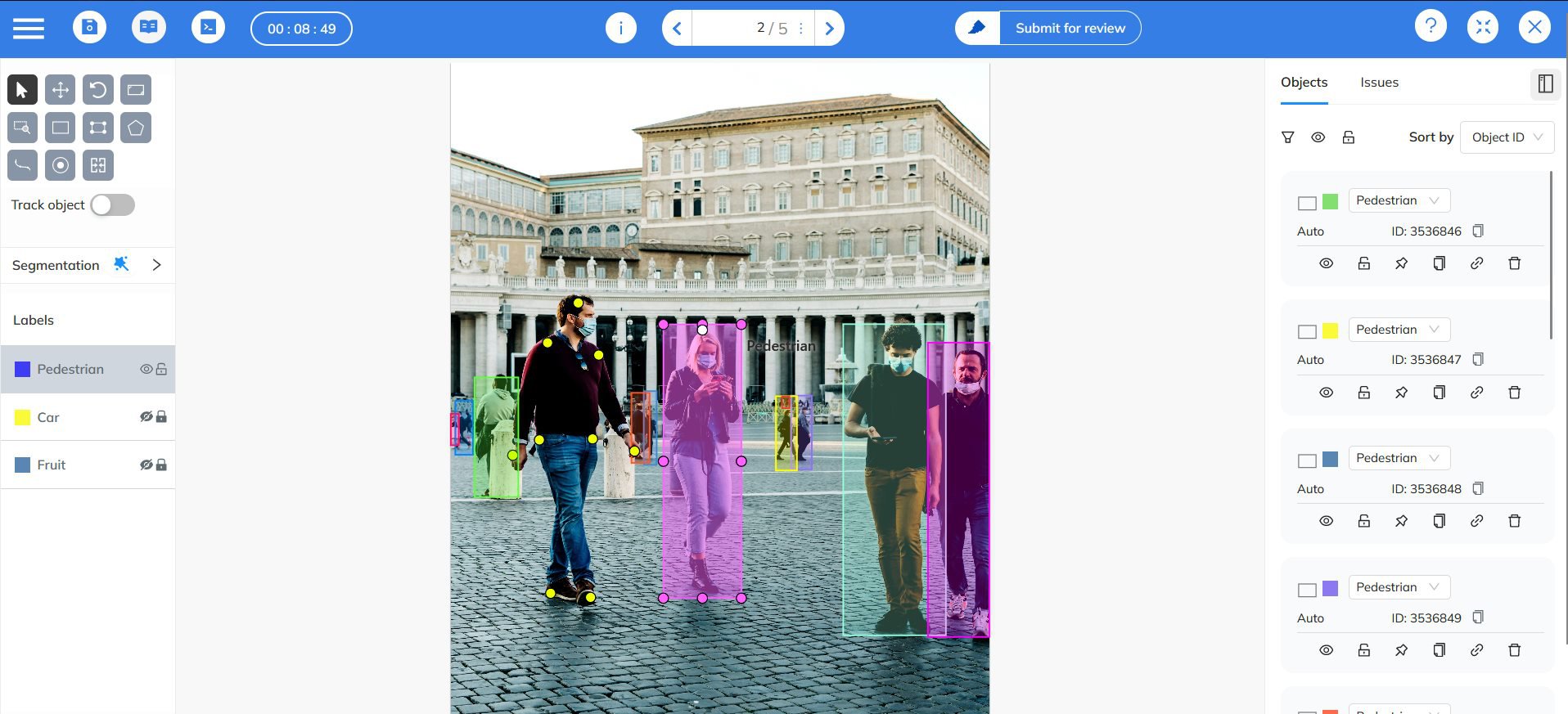
To build reliable datasets, Coral Mountain follows these core principles:
- Curated and Diverse Datasets
A well-balanced dataset that includes different lighting conditions, angles, ethnicities, ages, and body types ensures robustness.
- Exhaustive Guideline Documentation
Annotators receive guidelines with visual examples of correct and incorrect placements, rules for edge cases, and fallback criteria for ambiguous visuals.
- Layered Quality Control
- Peer review between annotators
- Supervisor validation
- Random sampling audits
- Automated error detection based on statistical deviation
- Human + AI Hybrid Approach
AI pre-labels frames where possible, and human annotators refine them. This drastically boosts efficiency without sacrificing precision.
- Ethical Responsibility
Consent-based usage, secure pipelines, and redaction of personally identifiable information (PII) are strictly enforced across Coral Mountain’s dataset workflows.
Use Cases for Keypoint Annotation
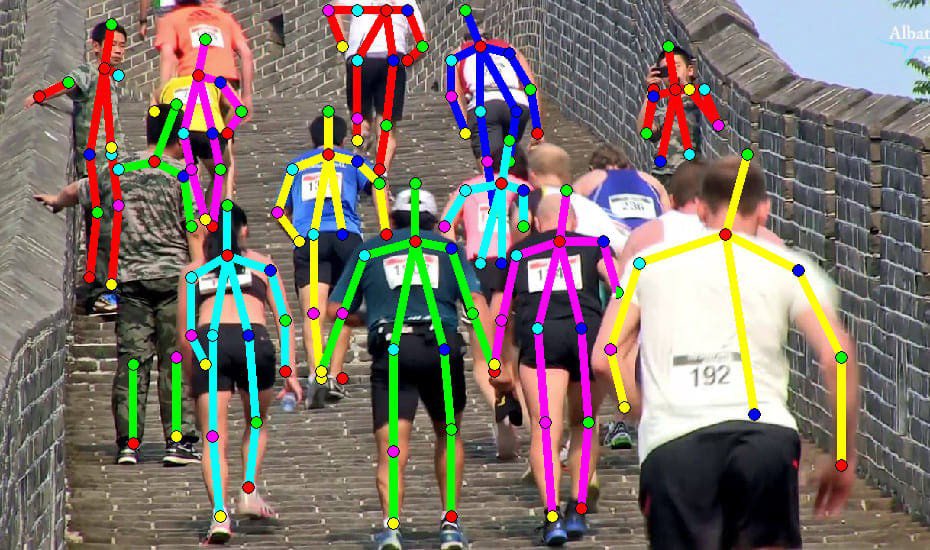

Keypoint annotation powers multiple fields across both consumer and enterprise applications:
- Human Pose Estimation
Used in:
- Sports analytics to improve athletic form
- Physiotherapy monitoring for patient recovery tracking
- Fitness apps to count repetitions and correct posture
- Facial Recognition & Expression Mapping
Supports:
- Identity verification systems
- Animation and virtual avatars in gaming and AR filters
- Emotion analysis in behavioral research
- Robotics and Autonomous Systems
Robots use keypoints to detect object orientation and manipulate them accurately. Autonomous vehicles use them to detect pedestrians and gestures in real time.
- Medical Annotation
Keypoints outline organ boundaries, tumor regions, and skeletal alignment, providing labeled data for diagnostics and treatment modeling.
- Surveillance and Security
Human motion tracking enables anomaly detection, such as falls, fights, or loitering behavior.
- Motion Capture & Entertainment
Film studios and game engines rely on skeletal keypoints to record actor movements and recreate them digitally.
- AR / VR Interaction
Keypoints transform body position into real-time input, enabling gesture-based interfaces in immersive environments.
Conclusion
Keypoint annotation is more than a labeling method—it is the foundation that allows machines to perceive movement, understand structure, and predict behavior. As AI advances across industries, demand for precise and ethically sourced keypoint datasets continues to surge.
With platforms like Coral Mountain, enterprises can scale annotation efficiently without compromising accuracy or compliance. Whether training pose estimation models, robotic perception systems, or interactive avatars, keypoint annotation acts as the connective tissue between raw images and intelligent interpretation.
Coral Mountain Data is a data annotation and data collection company that provides high-quality data annotation services for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models, ensuring reliable input datasets. Our annotation solutions include LiDAR point cloud data, enhancing the performance of AI and ML models. Coral Mountain Data provide high-quality data about coral reefs including sounds of coral reefs, marine life, waves….
Recommended for you
- News
Most remote work today faces the same underlying economic pressure: commoditization driven by automation and global...
- News
Explore how AVs learn to see: Key labeling techniques, QA workflows, and tools that ensure safe...
- News
How multi-annotator validation improves label accuracy, reduces bias, and helps build reliable AI training datasets at...
Coral Mountain Data
Office
- Group 3, Cua Lap, Duong To, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam
- (+84) 39 652 6078
- info@coralmountaindata.com
Data Factory
- An Thoi, Phu Quoc, Vietnam
- Vung Bau, Phu Quoc, Vietnam

Copyright © 2024 Coral Mountain Data. All rights reserved.