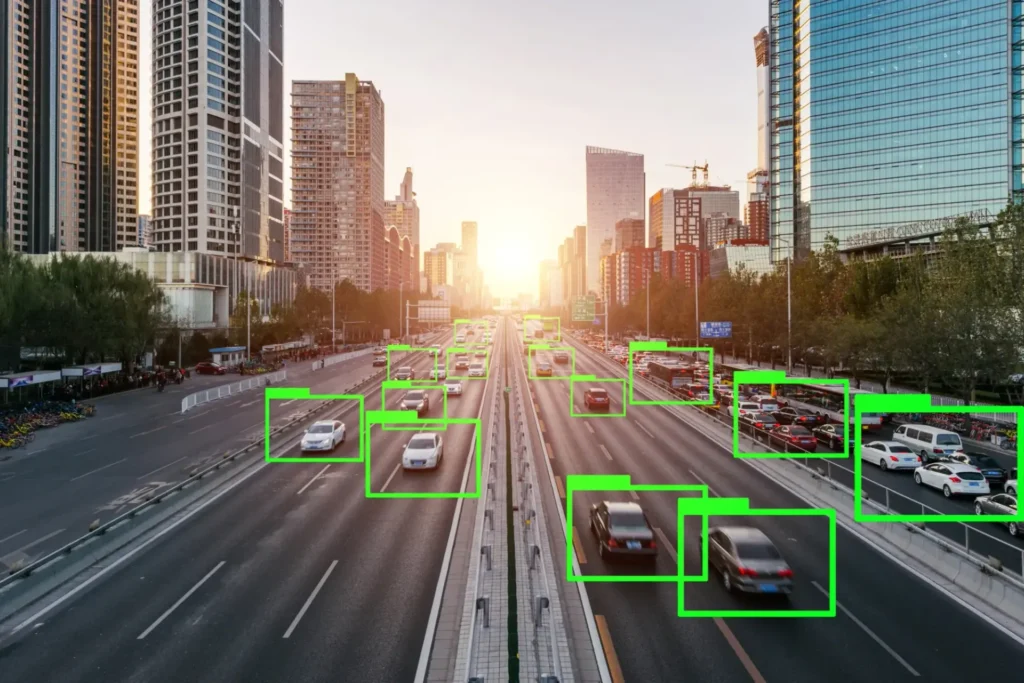
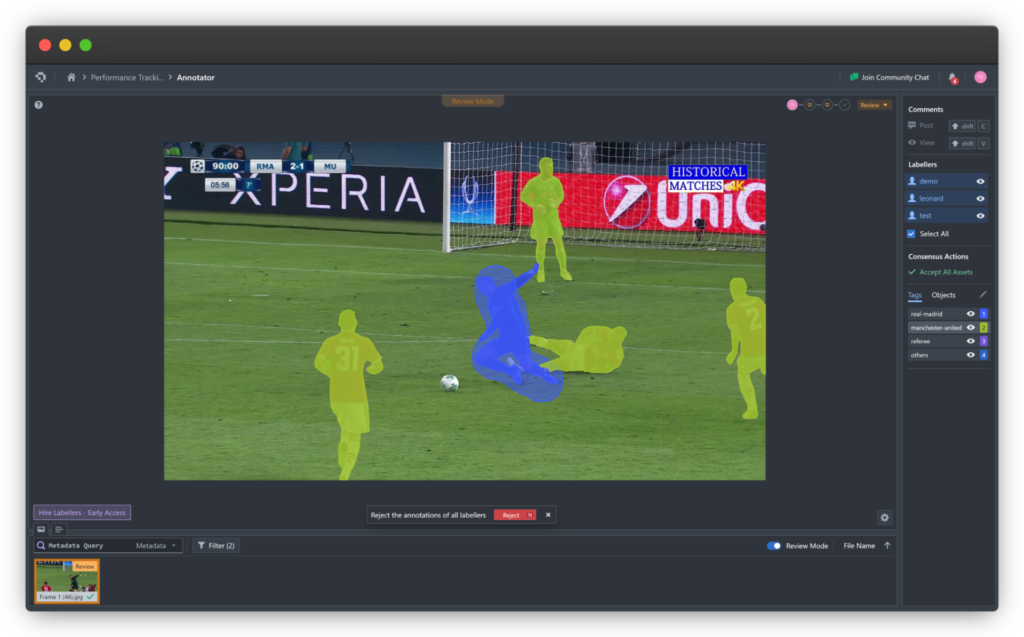
OCR image annotation transforms text in images into valuable data for NLP use-cases. Explore techniques, tools, and best practices for effective OCR data annotation.
Introduction

Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a transformative technology that converts various types of visual text — from scanned paper documents and PDFs to photos captured on mobile devices — into machine-readable data. As Natural Language Processing (NLP) continues to evolve, OCR has become increasingly vital in bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds of text.
In this article, we’ll explore how OCR image annotation supports NLP, its key techniques, tools, challenges, and the best practices that ensure accuracy and efficiency.
What is NLP?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a subfield of Artificial Intelligence that enables machines to interpret, understand, and generate human language. It powers applications like chatbots, translation systems, and sentiment analysis engines.
Traditionally, NLP tasks relied on specialized models for specific purposes. However, the rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) has unified these tasks under a single framework. Today, tasks such as Named Entity Recognition (NER), summarization, and sentiment analysis can all be performed by a single LLM across multiple languages and text types — revolutionizing how AI interacts with human language.
Common NLP Tasks
- Text Classification: Categorizing text into defined topics such as politics, sports, or finance.
- Entity Recognition: Identifying named entities (e.g., people, organizations, locations) or grammatical roles within sentences.
- Sentiment Analysis: Determining the emotional tone or polarity of text (positive, negative, neutral).
- Intent Detection: Recognizing user intent in queries — crucial for voice assistants like Siri or Alexa.
- Semantic Analysis: Understanding meaning, context, and relationships between words and phrases.
What is OCR?

OCR (Optical Character Recognition) converts printed, handwritten, or image-based text into editable and searchable digital data. It plays a crucial role in digitizing and organizing vast quantities of information.
Why OCR Matters for NLP
- Data Digitization
- Converts printed or handwritten text into structured digital form, making it accessible for NLP applications.
- Enables instant search and retrieval from large document archives.
- Document Processing
- Automates data extraction from invoices, contracts, and reports.
- Reduces manual labor in data entry, validation, and classification.
- Content Analysis
- Enables text categorization and sentiment analysis for feedback, reviews, or surveys.
- Provides insights into customer opinions and emerging trends.
- Accessibility and Inclusion
- Converts printed materials for use with screen readers, enhancing accessibility for visually impaired users.
- Supports real-time translation and multilingual content understanding when combined with NLP.
- Advanced AI Applications
- OCR-generated text is essential for training NLP and deep learning models.
- Enables real-time document verification, transcription, and automated support services.
- Integration with Other Technologies
- Works with IoT and AR systems for smart document scanning or contextual overlays.
- Enhances data processing in smart devices and automation platforms.
- Business Intelligence
- Extracts actionable insights from large unstructured text datasets.
- Facilitates trend analysis and strategic planning.
Annotating Data for OCR
Accurate data annotation is the foundation of high-performing OCR and NLP systems. Properly labeled data trains models to recognize, extract, and understand text efficiently. Below are the main methods used in OCR annotation:
Manual Annotation
Human annotators label text regions, characters, and structures.
- Pros: Very accurate, human contextual understanding.
- Cons: Time-intensive and expensive for large datasets.
Semi-Automatic Annotation
Uses pre-trained models or automation tools with human oversight.
- Pros: Faster than manual labeling; good accuracy.
- Cons: Requires skilled operators; potential inconsistency in labeling standards.
Fully Automatic Annotation
Automated pipelines detect and label text with minimal human intervention.
- Pros: Scalable, fast, and cost-efficient.
- Cons: Accuracy depends on data complexity and model performance.
Coral Mountain’s OCR annotation platform offers a fully automated annotation mode capable of detecting both the location and content of text within images. It supports annotation at different granularity levels — tokens, lines, or paragraphs — and works seamlessly with multiple global languages.
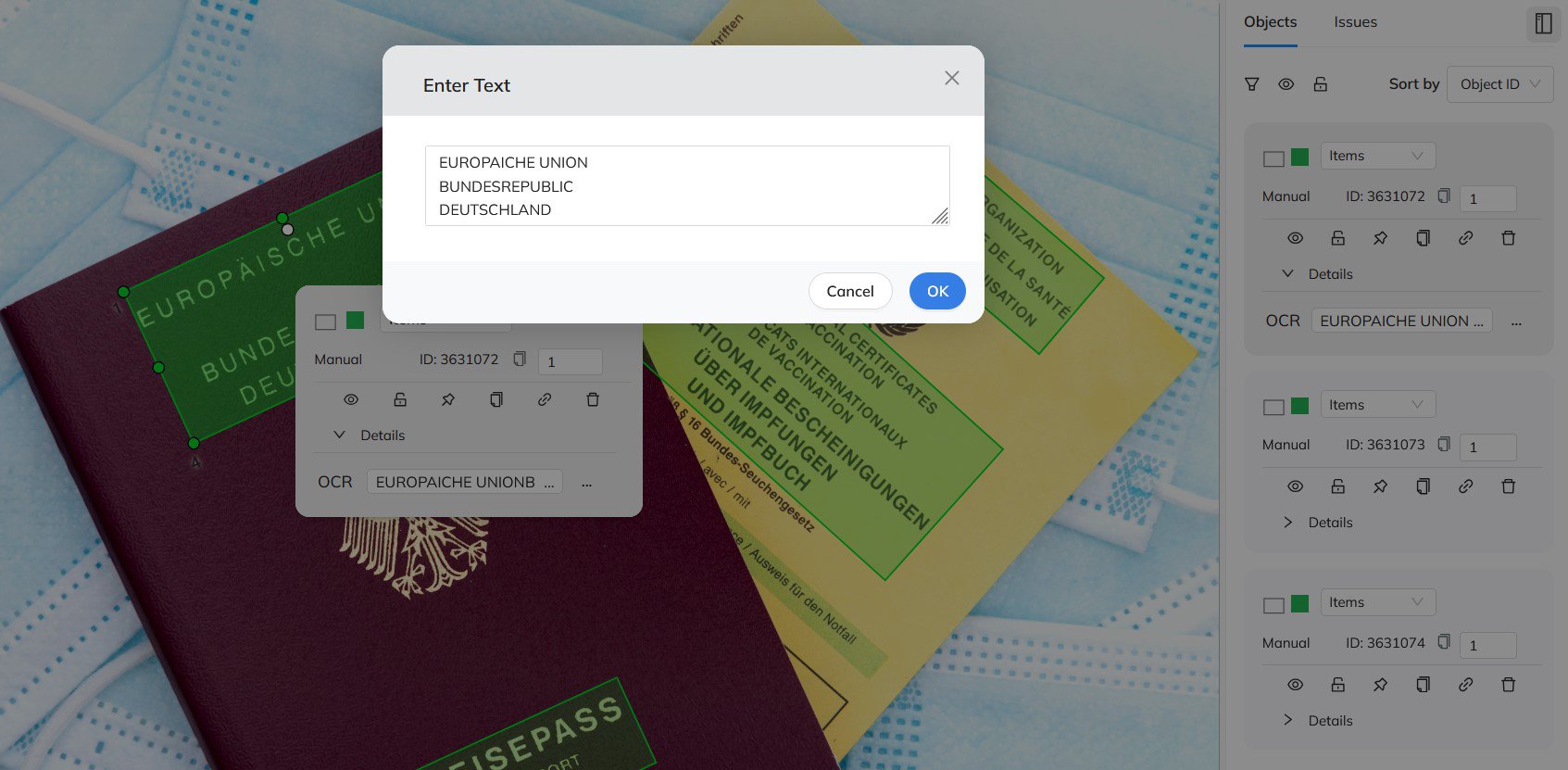
Best Practices for OCR Annotation
- Ensure High-Quality Scans
- Use high-resolution images (minimum 300 DPI) to maximize OCR accuracy.
- Select the Right Tools
- Choose OCR tools tailored for specific needs, such as handwriting or multi-language recognition.
- Validate and Review Regularly
- Implement multi-layer quality control to ensure data consistency.
- Leverage Metadata
- Include attributes like language, text source, and context for richer training data.
- Optimize Workflows
- Automate repetitive tasks and use workflow management tools for scalability.
Challenges in OCR Annotation

Despite its advantages, OCR technology faces several challenges that can affect NLP performance:
- Handwritten Text Variability: Diverse handwriting styles make recognition difficult.
- Complex Fonts and Layouts: Decorative fonts or irregular page layouts reduce accuracy.
- Low-Quality Images: Noise, blur, or distortion degrade recognition precision.
- Multilingual Documents: Multiple languages or scripts can confuse models.
- Annotation Inconsistency: Human errors and unclear guidelines lead to unreliable datasets.
Overcoming OCR Challenges
- Improve Recognition Accuracy
- Use deep-learning OCR models trained on diverse handwriting and font samples.
- Apply preprocessing techniques such as denoising and contrast enhancement.
- Enhance Multilingual Capabilities
- Incorporate multilingual language models and character recognition systems.
- Train on datasets rich in diacritics and special symbols.
- Add Context Awareness
- Use post-OCR NLP correction models to fix errors through contextual understanding.
- Employ hybrid OCR-NLP systems that analyze meaning and syntax simultaneously.
- Strengthen Annotation Quality
- Establish clear annotation guidelines and validation protocols.
- Use semi-automatic and AI-assisted annotation tools to ensure consistency.
Future Trends
- Smarter AI Models: Improved deep-learning OCR models will handle low-quality or complex documents more accurately.
- Deeper OCR-NLP Integration: Seamless data flow between OCR and NLP systems will enable faster, context-aware analysis.
- Cloud-Based Workflows: Cloud OCR solutions will make large-scale processing more accessible and cost-effective.
- Real-Time Processing: Instant OCR recognition will power live translation, data extraction, and real-time analytics.
Conclusion
OCR image annotation is a cornerstone of modern NLP — transforming static, unstructured text into actionable, machine-readable data. By combining robust annotation strategies with tools like Coral Mountain’s OCR platform, organizations can unlock the full potential of language-driven AI.
Staying ahead of trends and adopting best practices will ensure your OCR and NLP workflows remain efficient, scalable, and ready for the evolving digital landscape.
Recommended for you
- News
Most remote work today faces the same underlying economic pressure: commoditization driven by automation and global...
- News
Explore how AVs learn to see: Key labeling techniques, QA workflows, and tools that ensure safe...
- News
How multi-annotator validation improves label accuracy, reduces bias, and helps build reliable AI training datasets at...
Coral Mountain Data
Office
- Group 3, Cua Lap, Duong To, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam
- (+84) 39 652 6078
- info@coralmountaindata.com
Data Factory
- An Thoi, Phu Quoc, Vietnam
- Vung Bau, Phu Quoc, Vietnam

Copyright © 2024 Coral Mountain Data. All rights reserved.