Explore how AVs learn to see: Key labeling techniques, QA workflows, and tools that ensure safe and scalable autonomous driving.
Self-driving cars are no longer confined to science fiction. Today, they are quietly delivering packages, mapping urban environments, and navigating controlled test tracks. Yet the tr ue intelligence behind autonomous vehicles (AVs) does not lie in sleek hardware or advanced sensors alone-it lies in data, and more importantly, in how that data is labeled.
Every time an AV detects a traffic signal, slows down for a pedestrian, or merges into traffic, it is acting on patterns learned from vast amounts of labeled data. These datasets teach the system how to interpret its surroundings and respond appropriately.
Teaching an AV to drive is much like teaching a child how to cross the street. You point out cars, bicycles, traffic lights, and explain what each signal means. Autonomous vehicles learn in a similar way-but instead of verbal instructions, they rely on carefully labeled images, videos, and 3D point clouds.
The stakes are extremely high. A single labeling error can have serious consequences. For example, if a system fails to distinguish between a stroller and a lightweight object on the road, the outcome could be dangerous. In autonomous driving, data labeling is not a background task-it is the foundation of safety, reliability, and trust.
Key challenges when labelling data for autonomous driving
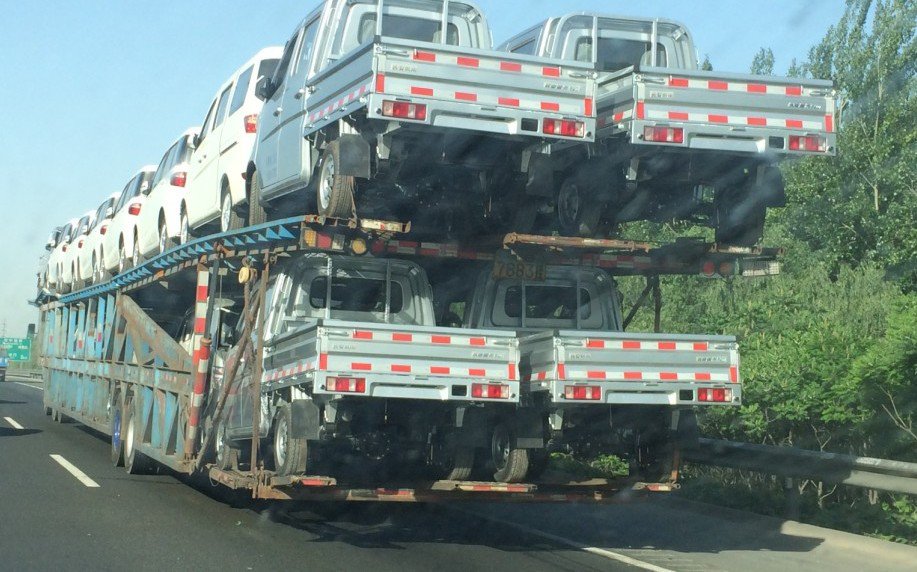

Although the objective is straightforward-help machines understand the world-the reality of labeling AV data is complex. From ambiguous scenes to rare edge cases, annotators face challenges that directly impact model performance.
Ambiguous scenarios & human oversight
The real world is rarely clean or predictable. Objects do not always appear in isolation or follow clear visual rules.
Consider a street sign mounted on a pole. Should the annotation include only the sign, the pole, or both? What if multiple signs-temporary and permanent-share the same structure? Inconsistent labeling decisions can introduce confusion during training.
Imagine an AV driving through a construction zone. A traffic cone is mistakenly labeled as a pedestrian. The vehicle reacts defensively and brakes abruptly, potentially causing an accident. This illustrates why human judgment and oversight remain critical.
Ambiguity in data demands contextual understanding-something humans still outperform machines at. On Coral Mountain, a robust issue-tracking dashboard allows annotators to flag such edge cases, ensuring reviewers can intervene before ambiguities propagate into training data.
Edge case complexity
Autonomous systems must handle rare events flawlessly. On the road, even a once-in-a-million scenario can be life-threatening.
Common edge cases include:
- Vehicles or pedestrians partially occluded by others
- Trucks transporting cars or motorbikes
- Snow-covered lane markings
- Fallen trees obstructing lanes
- Animals crossing roads during poor weather
- Children playing near parked vehicles
These situations are visually diverse and often underrepresented in datasets. When they do appear, annotators may be uncertain about how to label them correctly.
This is why specialized annotation guidelines and expert review processes are essential. Models trained only on ideal conditions struggle when faced with real-world complexity.
Discover how much your data annotation project might cost with our easy-to-use cost estimator. Visit our cost estimator page today to get a fast, accurate estimate tailored to your needs.
Annotation techniques used in AV development
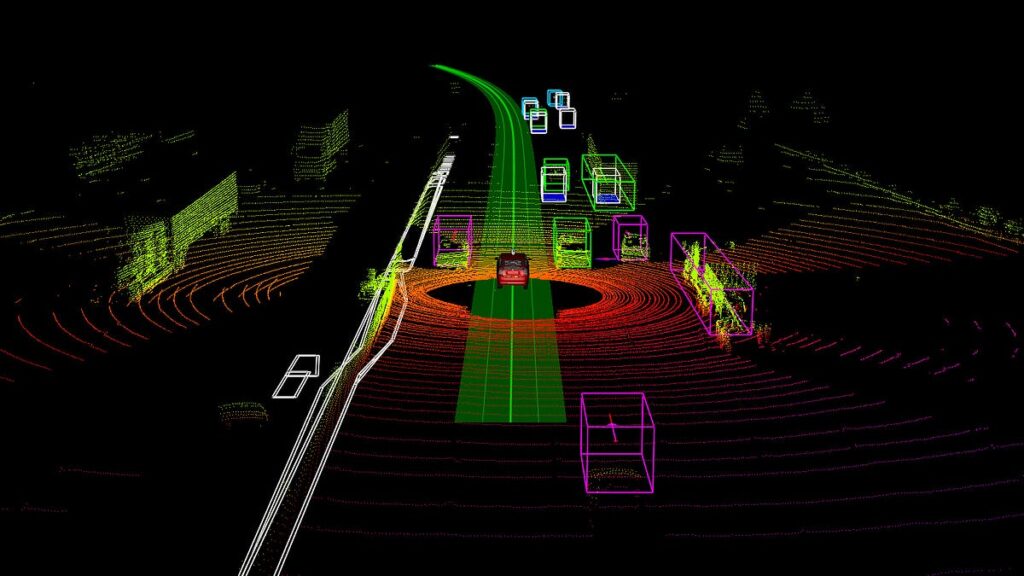
Autonomous vehicles rely on multiple sensors-cameras, LiDAR, radar, GPS-each producing different data formats. Teaching AVs to interpret this information requires a variety of annotation techniques, each serving a specific role.
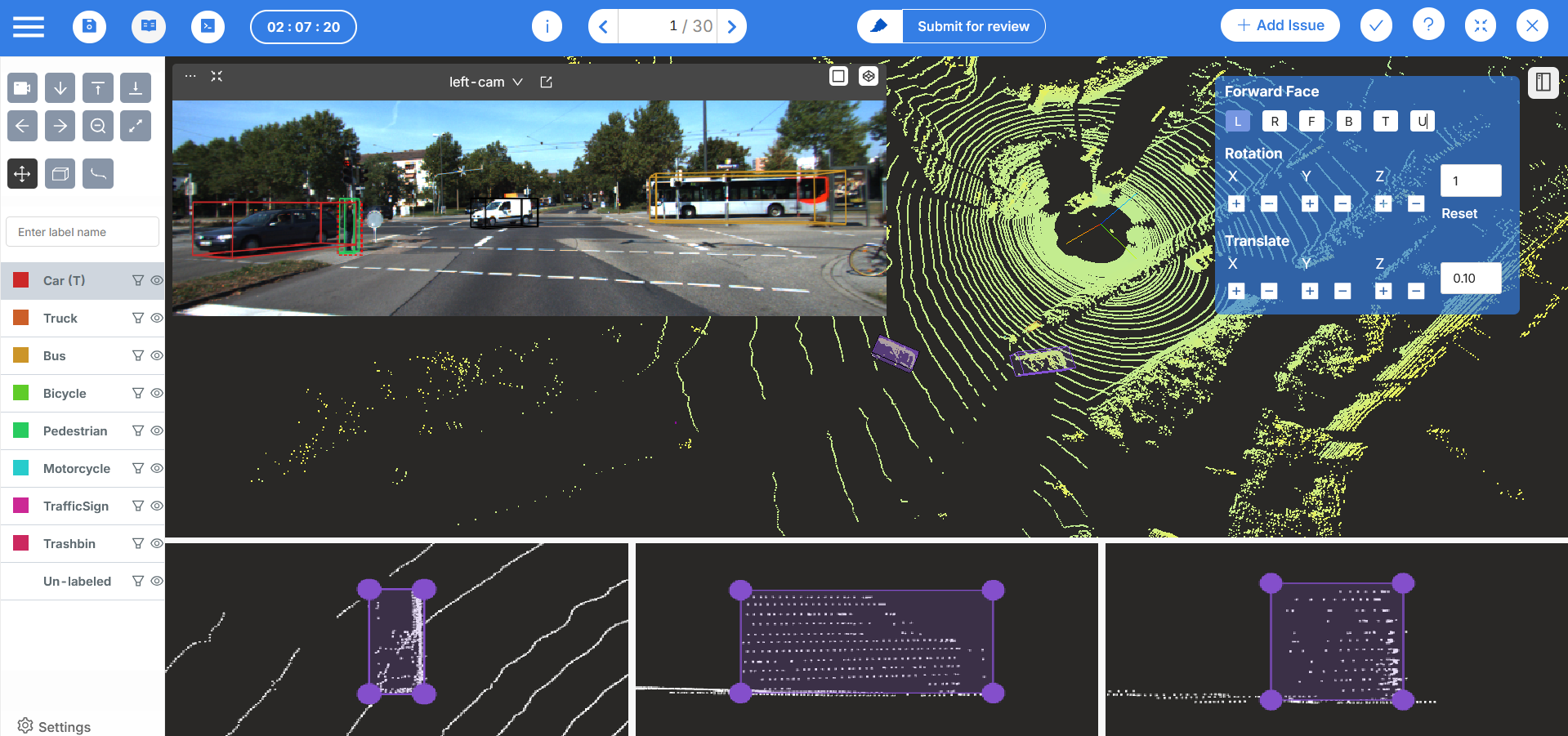
Bounding box annotation
Bounding boxes are one of the most widely used annotation techniques. Annotators draw rectangles around objects such as:
- Vehicles
- Pedestrians
- Bicycles
- Traffic signs
Bounding boxes are quick to create and effective for object detection tasks. When combined with object tracking, the same instance can be followed across video frames, improving temporal understanding while reducing redundant effort.
Interpolation techniques further boost efficiency by automatically generating bounding boxes between keyframes.
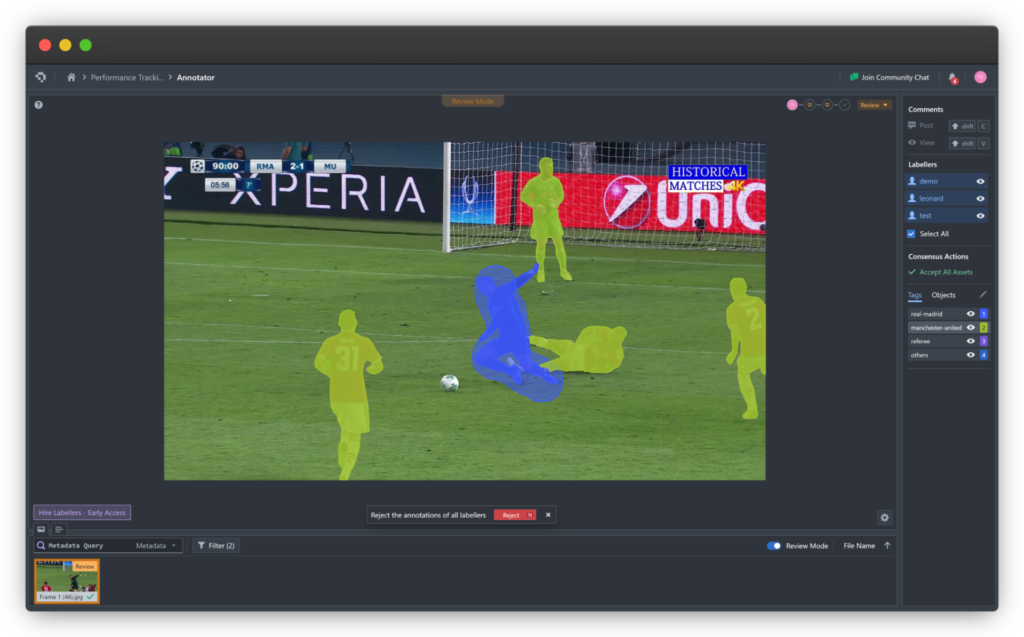
Semantic and instance segmentation
Bounding boxes provide coarse localization, but they do not capture precise object boundaries. Segmentation addresses this limitation.
Semantic Segmentation assigns a class label to every pixel, such as road, sidewalk, or vehicle.
Instance Segmentation goes further by distinguishing individual objects within the same class, such as separating two pedestrians standing close together.
In dense urban environments where occlusion is common, segmentation is essential. Precise object boundaries influence braking decisions, trajectory planning, and collision avoidance.
Polyline annotation
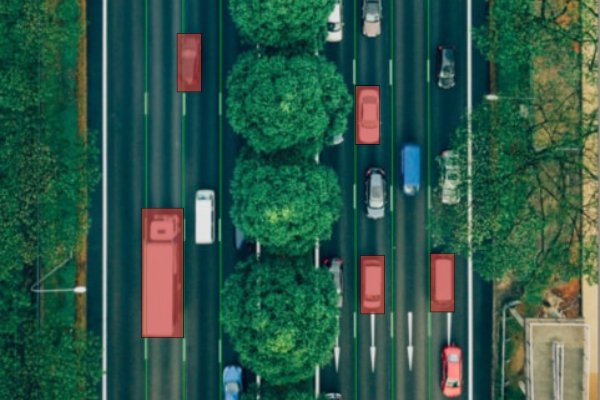

Polylines are used to annotate continuous structures, including:
- Lane markings
- Road edges
- Medians and dividers
- Sidewalk boundaries
These annotations help AVs understand where they are allowed to drive, how to stay centered in a lane, and when turns or lane changes are permitted. Inaccurate lane labeling can lead to drifting or unsafe maneuvers.
Annotation tools & automation: What enables scale?
If autonomous vehicles represent the future of transportation, annotation tools are the infrastructure that makes them possible.
Manually labeling a few hundred images is feasible, but production-grade AV systems require millions of annotations across multi-sensor datasets-images, videos, LiDAR point clouds, thermal and depth data.
Scaling annotation without sacrificing quality demands automation and intelligent tooling.
When choosing an annotation platform for AV or robotics use cases, key capabilities include:
- Support for multiple sensor types (LiDAR, radar, RGB, depth, thermal)
- Customizable workflows to enforce quality standards
- Automated annotation for segmentation and point clouds
- Strong team and task management
- Analytics to identify bottlenecks
- Ability to handle large teams and massive data volumes
Without the right platform, high-quality annotation at scale is virtually impossible-especially in autonomous driving, where both sensor complexity and quality requirements are high.
Coral Mountain provides a comprehensive suite of tools for AV data annotation. The platform supports LiDAR, radar, depth, thermal, and image data, along with automation features that significantly accelerate labeling while maintaining accuracy. Coral Mountain’s unified sensor-fusion interface enables consistent annotation across modalities, simplifying QA and improving dataset coherence.
Use cases in autonomous driving
Let’s explore how all this labeled data is ultimately used to advance autonomous driving systems.
Training robust machine learning models
At the core of every AV system is a machine learning model-but its effectiveness depends entirely on the quality of training data.
High-performing datasets must be:
- Diverse, covering varied geographies, weather, and lighting
- Accurate, minimizing mislabels
- Consistent, with clear rules for edge cases and object definitions
High-quality annotations enable models to:
- Detect and track objects reliably
- Estimate depth and distance
- Predict motion and trajectories
- Plan safe routes in real time
Establishing ground truth
Ground truth data serves as the benchmark for evaluating model predictions. It is used to:
- Measure accuracy
- Detect performance drift
- Drive iterative improvements
In simulation environments, ground truth allows developers to test AV behavior without real-world risk. Accurate labeling is what makes this possible.
Outsourcing at scale
Building an in-house annotation team is costly and time-consuming. As a result, many AV companies partner with specialized annotation providers.
A strong vendor brings:
- Experienced annotators trained on AV standards
- Scalable infrastructure
- Proven quality assurance workflows
However, not all vendors offer the same capabilities. Some excel at image annotation, while others have deeper expertise in multi-sensor data. Coral Mountain offers fully managed annotation solutions that combine a powerful platform with a skilled workforce, enabling teams to scale confidently without compromising quality.
Conclusion
In the race toward fully autonomous vehicles, attention often centers on AI breakthroughs and sensor hardware. Yet the true enabler of autonomy is data labeling.
Without labeled data, there is no perception.
Without perception, there is no autonomy.
Without autonomy, there is no self-driving future.
Data labeling teaches AVs how to interpret the world-to recognize that a stop sign demands action, that a child on a bicycle is a vulnerable road user, and that lane markings define non-negotiable boundaries.
It is meticulous, demanding work-but it is foundational. With the right tools, automation, and human expertise, data labeling can scale safely and reliably to meet the challenges of real-world driving.
So when you see a driverless car gliding down the street, remember that behind its seamless motion lies millions of human decisions-every box drawn, every line traced, and every pixel labeled-making autonomy possible.
Coral Mountain Data is a data annotation and data collection company that provides high-quality data annotation services for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models, ensuring reliable input datasets. Our annotation solutions include LiDAR point cloud data, enhancing the performance of AI and ML models. Coral Mountain Data provide high-quality data about coral reefs including sounds of coral reefs, marine life, waves, Vietnamese data…
Recommended for you
- News
How multi-annotator validation improves label accuracy, reduces bias, and helps build reliable AI training datasets at...
- News
Discover the world of point cloud object detection. Learn about techniques, challenges, and real-world applications. Introduction...
- News
Understand how far Lidar sensors can detect and the factors that influence their range, including sensor...
Coral Mountain Data
Office
- Group 3, Cua Lap, Duong To, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam
- (+84) 39 652 6078
- info@coralmountaindata.com
Data Factory
- An Thoi, Phu Quoc, Vietnam
- Vung Bau, Phu Quoc, Vietnam

Copyright © 2024 Coral Mountain Data. All rights reserved.