Discover the world of point cloud object detection. Learn about techniques, challenges, and real-world applications.
Introduction
Point cloud object detection is reshaping the way machines perceive and interpret three-dimensional environments. By enabling systems to understand spatial structure and object geometry, this technology plays a crucial role in modern 3D perception. This guide provides an in-depth overview of point cloud object detection, covering core concepts, commonly used methods, practical challenges, and emerging research directions.
What are Point Clouds?
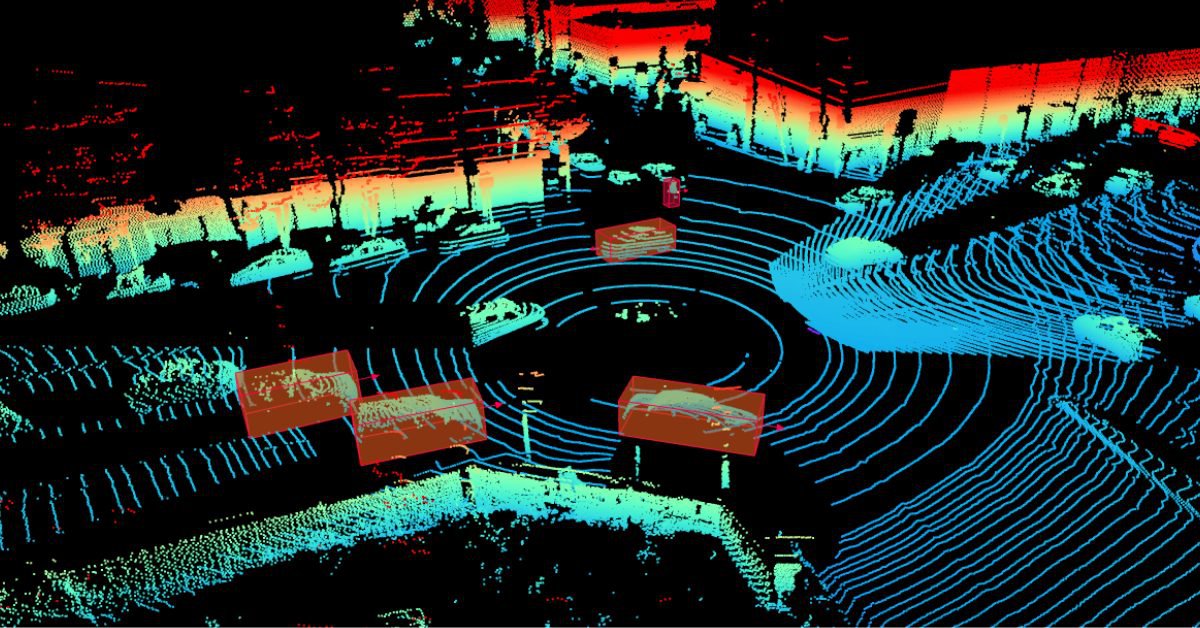
point cloud.jpg
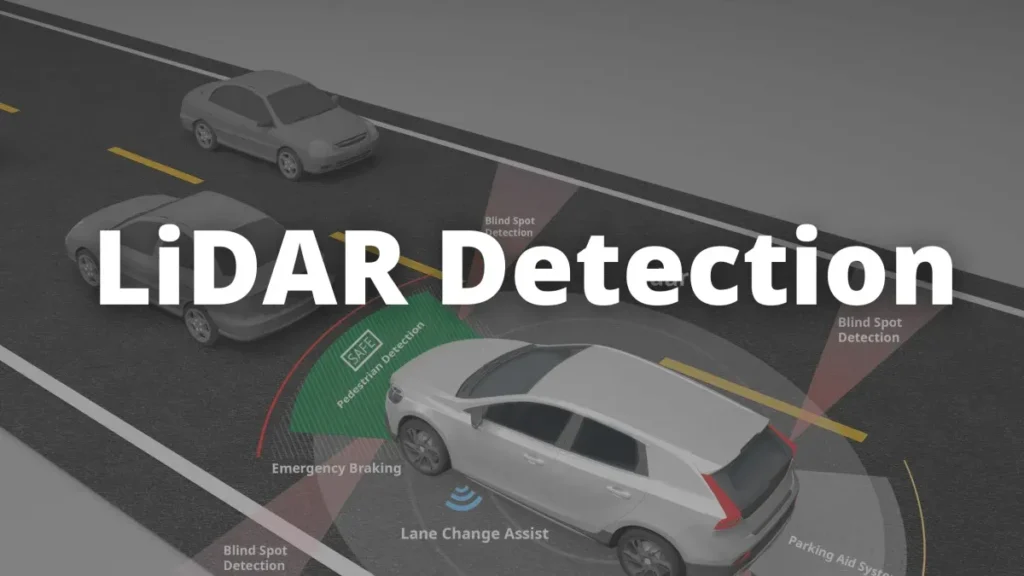
A LiDAR point cloud typically used in autonomous vehicle perception systems.
Point clouds consist of a large collection of points defined in three-dimensional space, representing the shape and surface of objects in the real world. These points are typically captured using sensing technologies such as LiDAR, where each point encodes spatial coordinates and sometimes additional attributes like intensity or color. Together, they form a detailed geometric representation of the environment, offering valuable insight into object structure and positioning.
Why is Point Cloud Object Detection Important?
Accurately identifying and localizing objects within point clouds is essential for applications that rely on spatial awareness and real-time decision-making, including:
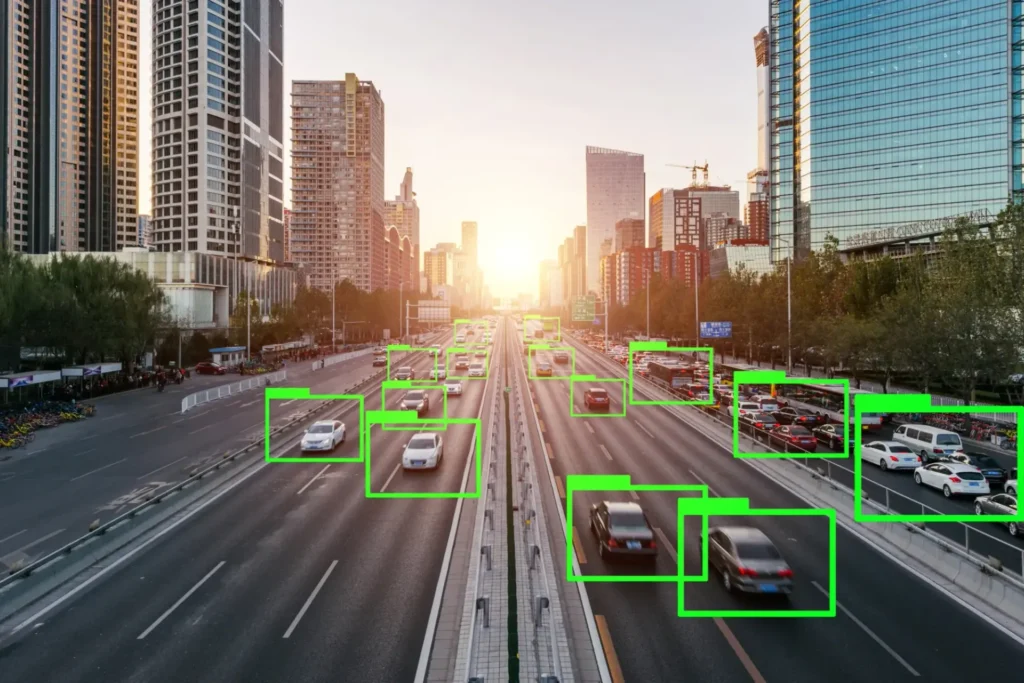
- Autonomous Driving: Improves vehicle perception, navigation, and obstacle avoidance.
- Robotics: Enables robots to recognize, grasp, and manipulate objects in dynamic environments.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Enhances depth understanding for more realistic and immersive user experiences.
- Computer Vision: Supports comprehensive 3D scene interpretation beyond traditional 2D imagery.
Discover a wealth of knowledge with our curated collection of ebooks and whitepapers. Visit our resources page to gain insights and stay ahead in your field.
Acquisition Methods
Point clouds are generated through several widely used sensing approaches:
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): Delivers highly accurate, long-range measurements. LiDAR-generated point clouds are typically dense, making them well suited for object detection tasks.
- Depth Cameras: Capture depth information directly and are commonly used for indoor environments and close-range mapping.
- Stereo Vision: Uses paired cameras to estimate depth, offering a cost-effective solution for mobile devices and AR applications.
Challenges and Limitations of Point Cloud Data
Despite their richness, point cloud datasets present several challenges. Sparsity, sensor noise, and large data volumes can complicate processing, particularly for real-time systems. Effective object detection depends on robust algorithms capable of handling these limitations while maintaining accuracy and efficiency.
Calculating point cloud features
Point Descriptors
Fast Point Feature Histograms
FPFH is a streamlined and efficient variant of the Point Feature Histogram (PFH). It captures local surface characteristics by analyzing geometric relationships between neighboring points, while significantly reducing computational overhead. This makes FPFH especially suitable for time-sensitive applications.
Point Feature Histograms
PFH is a powerful 3D feature descriptor that encodes detailed local geometry by examining spatial relationships among points and their neighbors. While highly descriptive and effective for object recognition, PFH is computationally expensive, which can limit its use in large-scale or real-time scenarios.
Feature Extraction Techniques
Max Pooling
Max pooling is a widely used feature extraction strategy in point cloud processing. It selects the maximum value from a group of features—often derived from neighboring points—to represent that region. This approach reduces data dimensionality while preserving the most significant geometric features.
Multi-Patch Feature Extraction
Multi-patch feature extraction segments a point cloud into multiple overlapping patches and extracts features from each one independently. By considering multiple local contexts, this method captures finer geometric details and is particularly effective for complex object shapes.
Point Cloud object detection methods

Traditional Methods
Classical point cloud object detection approaches rely on deterministic algorithms to separate and identify structures within the data. Two of the most commonly used methods are:
RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus)
RANSAC is an iterative technique that fits geometric models—such as planes or cylinders—to subsets of point cloud data while rejecting outliers. Its robustness to noise makes it highly effective in real-world environments, and it is frequently used for tasks like ground plane detection.
Hough Transform
The Hough Transform identifies geometric shapes by mapping points into a parameter space, where patterns such as lines or circles appear as peaks. It is well suited for structured scenes but can become computationally demanding when applied to complex geometries.
Deep Learning-based Methods
Recent advances in deep learning have significantly improved point cloud object detection performance:
- PointNet: Introduced direct processing of unordered point sets, laying the foundation for deep learning on point clouds.
- VoxelNet: Converts point clouds into voxel representations and applies convolutional networks for 3D detection.
- PointRCNN: Uses a region-based CNN framework to achieve highly accurate object localization.
Comparison and Evaluation of Different Methods
When evaluating object detection approaches, factors such as detection accuracy, computational cost, and robustness to noise are critical. For instance, PointRCNN offers high localization precision but generally requires more computational resources than lighter architectures like PointNet.
Challenges and considerations
Noise and outliers in Point Clouds
Noise and outliers can significantly impact detection reliability. Preprocessing steps such as filtering, normalization, and statistical analysis are essential for removing erroneous points and improving overall data quality.
Occlusion and clutter
In real-world scenes, objects often overlap or partially obscure one another. This occlusion, combined with cluttered environments, makes object separation difficult. Advanced methods such as multi-view fusion help mitigate these challenges by combining information from different perspectives.
Computational complexity
Real-time object detection requires efficient handling of large point cloud datasets. Techniques like down-sampling, voxelization, and data compression are commonly used to reduce processing demands without significantly affecting accuracy.
Evaluation Metrics
Object detection performance is typically assessed using the following metrics:
- Intersection over Union (IoU): Evaluates localization accuracy by measuring the overlap between predicted and ground-truth objects.
- Precision: Indicates how many detected objects are correct, with higher precision meaning fewer false positives.
- Recall: Measures the ability to detect all relevant objects, where higher recall corresponds to fewer missed detections.
Future trends and research directions
Novel Deep Learning architectures
New architectures continue to emerge with a focus on efficiency and scalability, making point cloud processing feasible on resource-constrained platforms such as drones and edge devices.
Real-time Point Cloud processing
With growing demand in autonomous driving and robotics, research increasingly targets low-latency pipelines capable of delivering rapid, reliable perception for real-time decision-making.
Multi-modal Fusion
Combining point clouds with visual data from cameras or other sensors leads to richer environmental representations. Multi-modal fusion enhances spatial understanding and improves detection robustness, forming a key direction for future perception systems.
Coral Mountain Data is a data annotation and data collection company that provides high-quality data annotation services for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models, ensuring reliable input datasets. Our annotation solutions include LiDAR point cloud data, enhancing the performance of AI and ML models. Coral Mountain Data provide high-quality data about coral reefs including sounds of coral reefs, marine life, waves….
Recommended for you
- News
Explore how AVs learn to see: Key labeling techniques, QA workflows, and tools that ensure safe...
- News
How multi-annotator validation improves label accuracy, reduces bias, and helps build reliable AI training datasets at...
- News
Understand how far Lidar sensors can detect and the factors that influence their range, including sensor...
Coral Mountain Data
Office
- Group 3, Cua Lap, Duong To, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam
- (+84) 39 652 6078
- info@coralmountaindata.com
Data Factory
- An Thoi, Phu Quoc, Vietnam
- Vung Bau, Phu Quoc, Vietnam

Copyright © 2024 Coral Mountain Data. All rights reserved.