Discover how 2D cuboid annotation can enhance object detection accuracy. Learn best practices, tools, and techniques for annotating 3D objects, and improve your AI and machine learning models with precise cuboid annotations.
This article focuses on cuboid annotation for 2D images. If you’re looking for information on 3D cuboid annotation for point clouds, please refer to Coral Mountain’s dedicated guide.
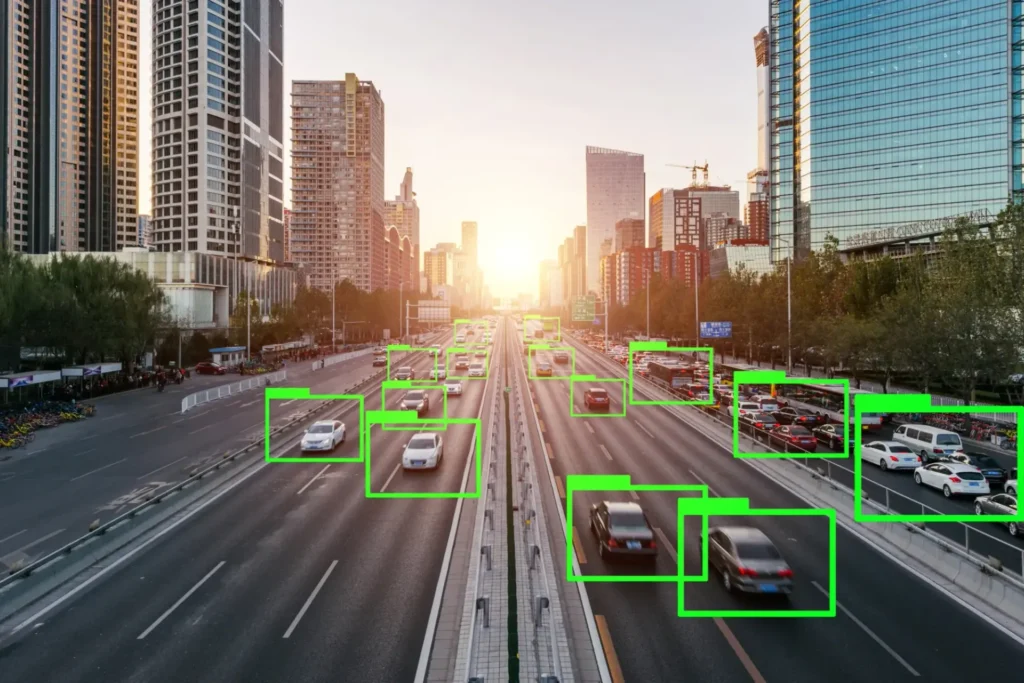
Traditional labeling techniques such as bounding boxes lack a critical component—depth perception. 2D cuboid annotation fills this gap by converting flat images into spatially aware, three-dimensional representations. It provides machine learning models with depth information and spatial understanding necessary for accurate interpretation of real-world environments. In this article, we’ll explore what makes cuboid annotation so impactful, its main benefits, key applications, and the best methods for implementation.
What Advantages Does Cuboid Annotation Offer?

Enhancing Depth Perception
While humans perceive depth naturally, most cameras and AI systems operate on a flat, 2D plane. Cuboid annotation bridges this gap by encoding 3D geometry into 2D images or videos. Annotators draw cuboids that define an object’s orientation, scale, and position, allowing AI models to interpret not only what an object is but also where it is in space.
This is particularly important for applications like autonomous driving or robotics, where understanding distances and spatial relationships is essential for decision-making.
Supporting Supervised Learning
Cuboid annotation plays a vital role in supervised machine learning, where models are trained on labeled datasets. By tagging thousands of 2D images with 3D cuboids, annotators provide examples that teach models to recognize and interpret spatial cues.
When trained on high-quality cuboid data, AI systems can generalize effectively to new environments and handle diverse object orientations, lighting conditions, and occlusions.
Reducing Bias in AI Systems
Bias often stems from limited or unbalanced datasets. Cuboid annotation allows for the creation of diverse, complete datasets that better represent real-world variability. By including objects of different types, sizes, and perspectives, annotators ensure that the model learns from a balanced dataset—reducing the risk of skewed or inaccurate predictions.
Annotating 2D Images with Cuboids

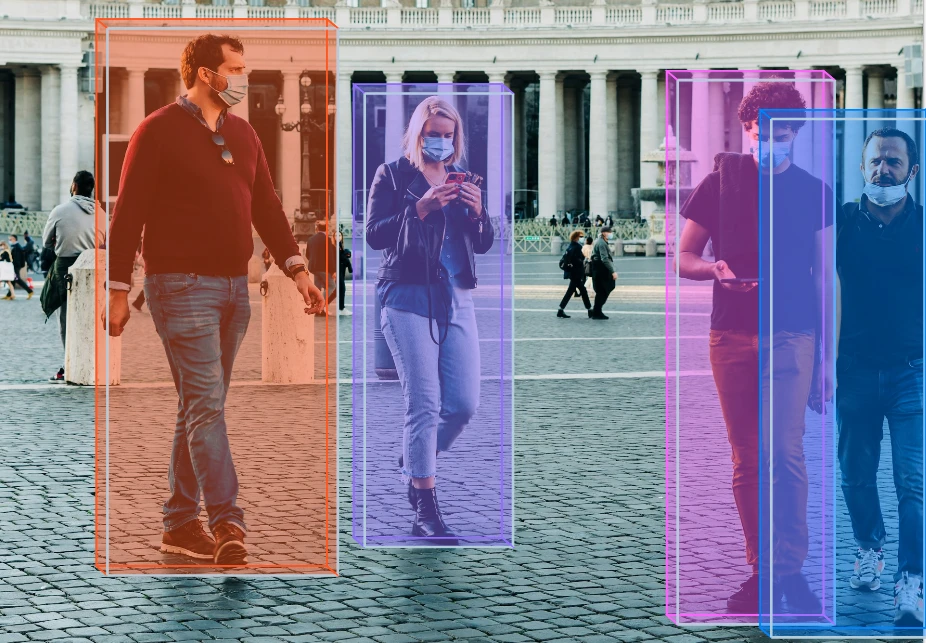
Manual Annotation
Manual cuboid labeling involves human experts carefully outlining the depth and dimensions of objects in 2D imagery. This approach ensures maximum precision and reliability, as human annotators can make context-based judgments that algorithms might miss.
However, it’s also labor-intensive and time-consuming, especially for complex datasets with overlapping objects or irregular shapes. Projects requiring the highest accuracy often rely on multiple annotators and validation methods such as inter-annotator agreement to maintain consistency.
Automated Annotation
Automated cuboid annotation uses advanced AI-assisted algorithms to identify and label objects without human intervention. This approach is highly scalable and efficient for large datasets. However, fully automated cuboid labeling is still a developing field that requires significant computational resources and infrastructure to maintain accuracy.
In most cases, semi-automated workflows—where human annotators refine AI-generated cuboids—offer the best balance between speed and precision.
Applications of Cuboid Annotation
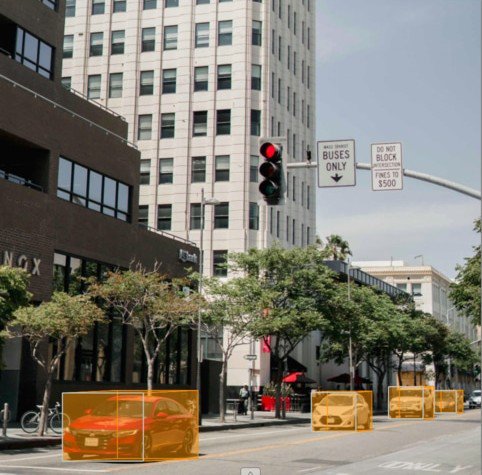
Autonomous Vehicles
Cuboid annotation is fundamental in training AI for autonomous driving systems. It enables self-driving cars to perceive their surroundings accurately by detecting vehicles, pedestrians, road signs, and other objects in three-dimensional space.
- Distance Estimation: Helps the system calculate object distance and relative speed.
- Collision Avoidance: Improves detection accuracy, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Traffic Sign Recognition: Allows ML models to interpret signs and signals more reliably.
Indoor Object Detection
In environments like homes, offices, or warehouses, cuboid annotation helps AI systems understand spatial relationships between objects.
- Smart Homes: Assists in object identification and navigation for AI assistants.
- Warehouse Automation: Guides robots to detect, pick, and place items accurately.
Robotics
Robots in manufacturing or logistics rely heavily on spatial understanding. Training with cuboid annotations enables them to grasp and manipulate objects with precision.
- Manufacturing: Ensures accurate part recognition and assembly.
- Logistics: Helps robots stack items safely and efficiently.
Medical Imaging
Cuboid annotation in medical images supports organ segmentation, tumor detection, and surgical planning by providing contextual 3D structure—enhancing diagnostic accuracy and treatment precision.
AR/VR
In augmented and virtual reality, cuboid annotation enables more immersive experiences by improving object recognition, spatial mapping, and interaction accuracy.
Challenges in Labeling Images with Cuboids
Depth Estimation
One of the most complex aspects of 2D cuboid labeling is inferring depth from flat images. Unlike 3D scans, 2D data lacks inherent depth information, requiring annotators to rely on visual cues such as lighting, shadow, and perspective. This can lead to inconsistencies, especially in images with overlapping objects or distorted angles.
Maintaining Consistency
Different annotators may interpret object orientation or size differently, leading to inconsistent cuboid placement. Establishing annotation guidelines and periodic quality reviews is essential for uniform results across large datasets.
Cost and Complexity
Because of the expertise required, manual cuboid annotation can be expensive. It involves specialized tools, skilled personnel, and extensive quality checks—all of which add to project costs.
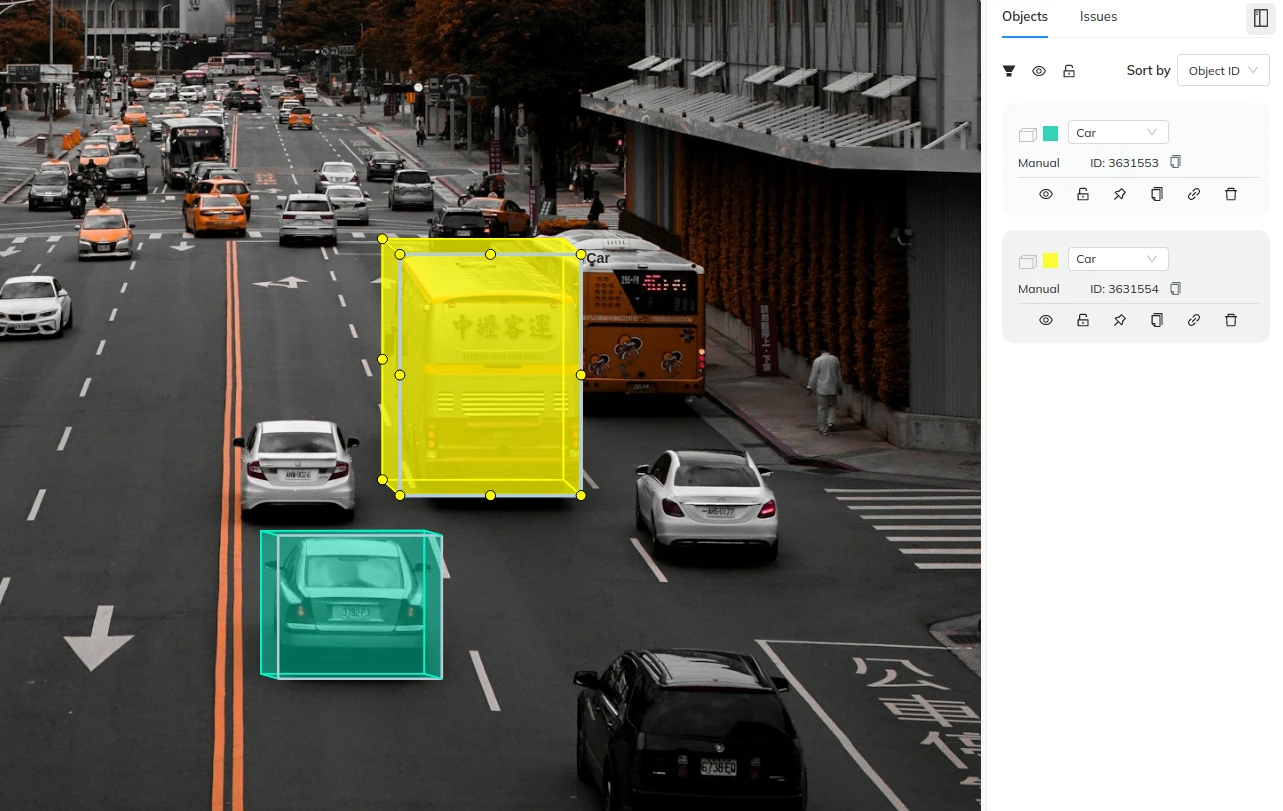
A powerful platform like Coral Mountain’s Annotation Suite simplifies this process. The platform allows direct manipulation of cuboids by adjusting front and rear faces intuitively, ensuring precise control over depth and position. For video data, automatic interpolation between frames accelerates labeling, allowing annotators to focus on keyframes while maintaining continuity.
In addition, Coral Mountain offers advanced dataset management and quality assurance features—crucial for large-scale annotation projects that require consistency, speed, and reliability.
Conclusion
Cuboid annotation is a cornerstone technique in modern computer vision, bridging the gap between 2D imagery and 3D spatial understanding. Its applications span from autonomous vehicles and robotics to healthcare and AR/VR development. By providing AI systems with a richer spatial context, cuboid annotation enables more accurate object detection, better decision-making, and safer automation.
As annotation tools and machine learning frameworks continue to evolve, Coral Mountain remains at the forefront—developing intelligent solutions to make 3D understanding more accessible, efficient, and precise.
Recommended for you
- News
Most remote work today faces the same underlying economic pressure: commoditization driven by automation and global...
- News
Explore how AVs learn to see: Key labeling techniques, QA workflows, and tools that ensure safe...
- News
How multi-annotator validation improves label accuracy, reduces bias, and helps build reliable AI training datasets at...
Coral Mountain Data
Office
- Group 3, Cua Lap, Duong To, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam
- (+84) 39 652 6078
- info@coralmountaindata.com
Data Factory
- An Thoi, Phu Quoc, Vietnam
- Vung Bau, Phu Quoc, Vietnam

Copyright © 2024 Coral Mountain Data. All rights reserved.