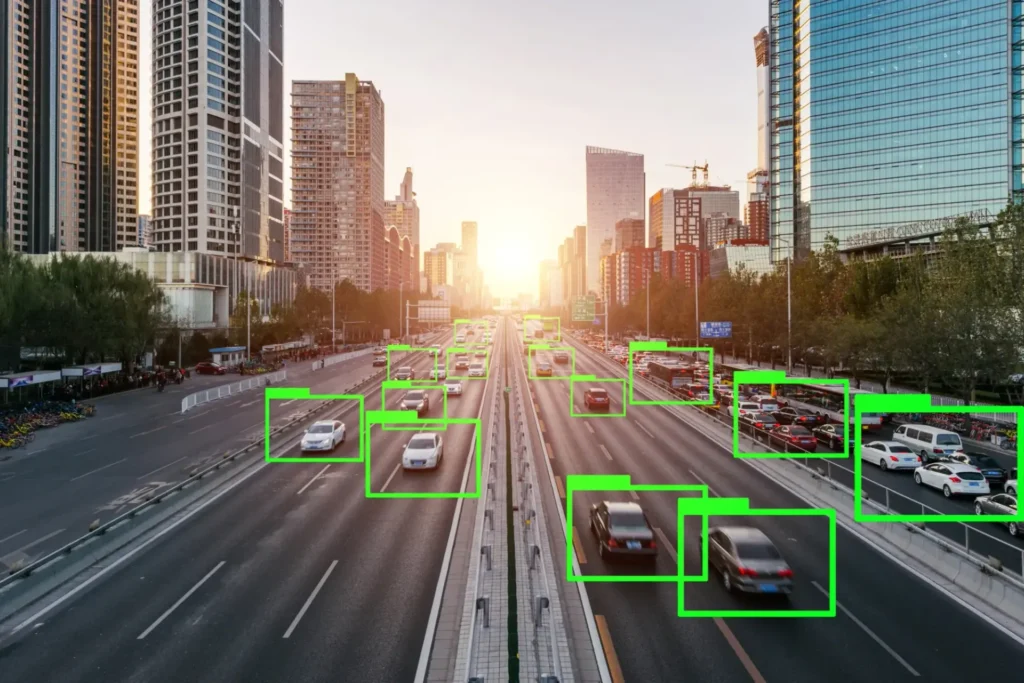
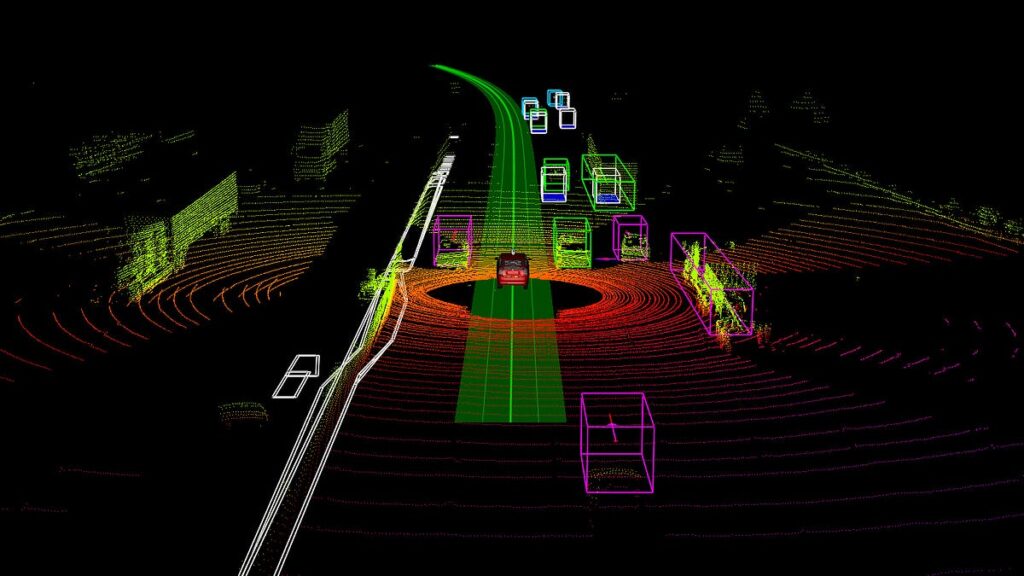
Lidar technology has rapidly expanded across multiple industries thanks to major advancements in sensor capability, improved processing power, and a significant reduction in cost. Below is an expanded look at how Lidar is being applied today.
Introduction to Lidar
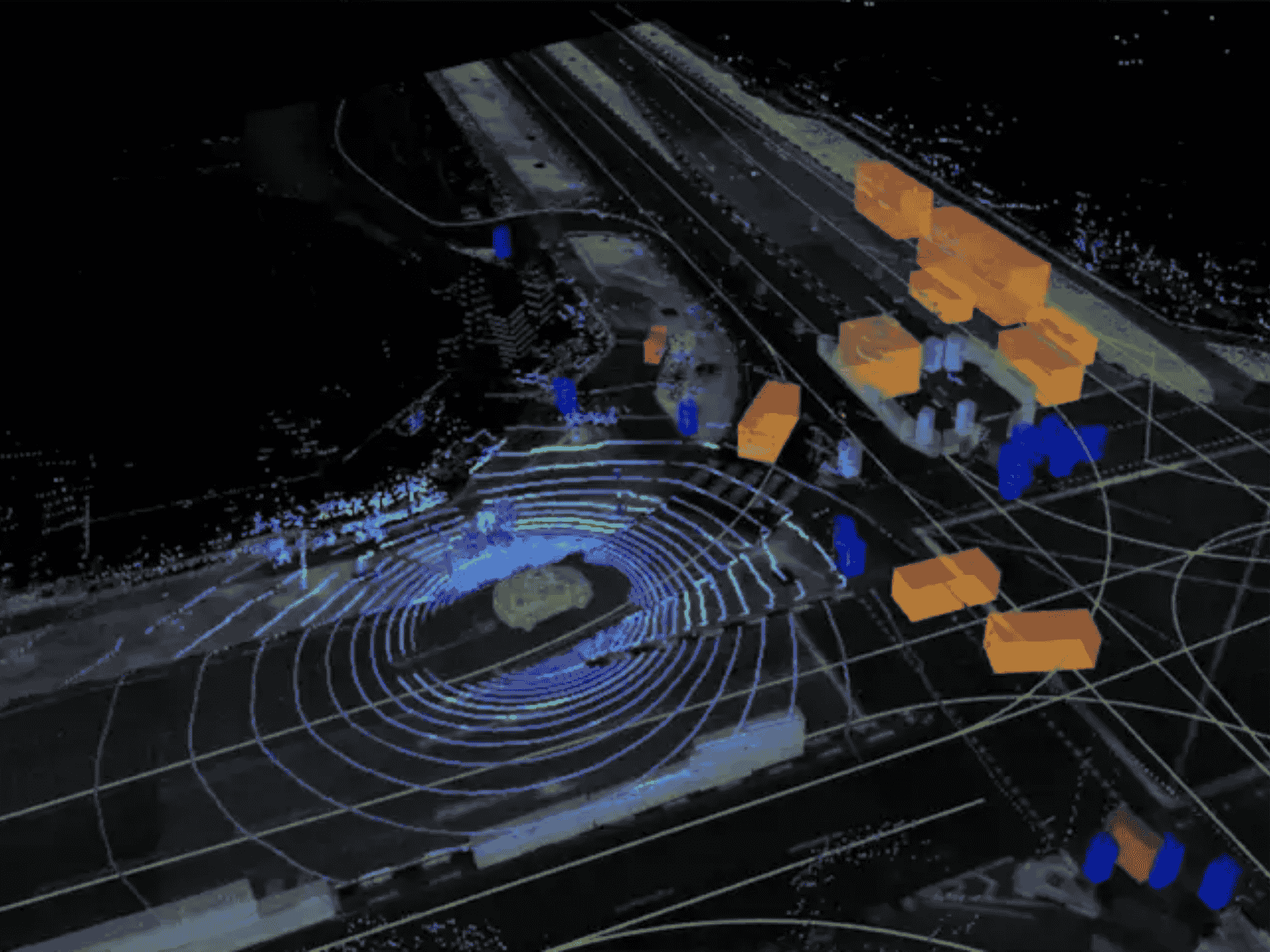
Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing method that uses laser pulses to measure distances and build detailed 3D representations of objects and environments. By sending out laser beams and calculating how long they take to return, Lidar systems generate highly accurate point clouds—often capturing millions of data points per second.
Its precision and reliability make Lidar indispensable in fields ranging from autonomous transportation to environmental science. As Lidar sensors have become more affordable and advanced, their real-world applications have grown exponentially.
Advantages of Lidar
Resolution
Lidar delivers extremely high-resolution spatial data, enabling detailed environmental modeling. With the ability to detect very small objects and fine structural differences, Lidar is ideal for mapping and analytical applications requiring high precision.
Range
Modern Lidar systems can measure long distances with exceptional accuracy—often spanning several hundred meters with sub-centimeter precision. This makes them valuable for large-scale mapping and long-range detection tasks.
Real-time Data
The ability to collect data in real-time is one of Lidar’s strongest advantages. Applications such as self-driving vehicles rely on constant, instant updates of the surrounding environment to ensure safety and reliability.
Weather Conditions
Unlike camera-based systems that struggle in low light, fog, or glare, Lidar performs consistently in a wide range of lighting and weather conditions—even total darkness. This makes it a dependable option for mission-critical applications.
Why Lidar is being rapidly adopted
Improved Accuracy
Lidar offers superior measurement accuracy compared to many alternative sensing technologies. When paired with advanced processing algorithms, Lidar becomes a cornerstone for applications that require dependable spatial awareness.
Reduced Costs
The cost of Lidar hardware has dropped dramatically due to advancements in semiconductor manufacturing and higher production volumes. This increased affordability has enabled broader adoption—including consumer electronics like smartphones.
Integration with AI
Combining Lidar with AI and machine learning unlocks powerful insights. For instance, Lidar data supports object classification in autonomous vehicles, or helps environmental scientists detect changes in deforestation with remarkable accuracy.
Applications across various industries

Lidar’s adaptability enables its use in a wide range of domains. Below are nine major industries where Lidar is driving transformation.
Autonomous Vehicles
Lidar is essential for self-driving technology, offering vehicles a 3D understanding of their environment.
- Object Detection and Avoidance
Continuous scanning allows vehicles to detect cars, pedestrians, and road obstacles, predict their movement, and navigate safely. - Mapping
High-definition maps created from Lidar data support accurate routing and help vehicles adjust to real-world changes.
Construction and Engineering
- Site Mapping
Lidar captures topography, building structures, and vegetation in detail—supporting precise land surveys and engineering analyses. - Progress Monitoring
Engineers compare Lidar scans with design plans to track project status and detect deviations early.
Robotics
- Autonomous Navigation
Robots use Lidar to understand surroundings, avoid obstacles, and move safely without human control. - Industrial Automation
Warehouse and manufacturing robots depend on accurate spatial data to transport goods or complete tasks efficiently.
Environmental Monitoring
Lidar is a powerful tool for studying ecosystems and detecting environmental changes.
- Forest Mapping
Scientists analyze tree height, biomass, and canopy structure to assess forest health and detect deforestation. - Land Cover Analysis
Lidar supports classification of land use changes, from urban development to agricultural expansion.
Defense & Military Applications
- Target Detection
Lidar’s high-resolution imagery assists in mission planning, reconnaissance, and identifying threats. - Mapping & Surveillance
The ability to map rugged or inaccessible terrain makes Lidar invaluable for tactical operations.
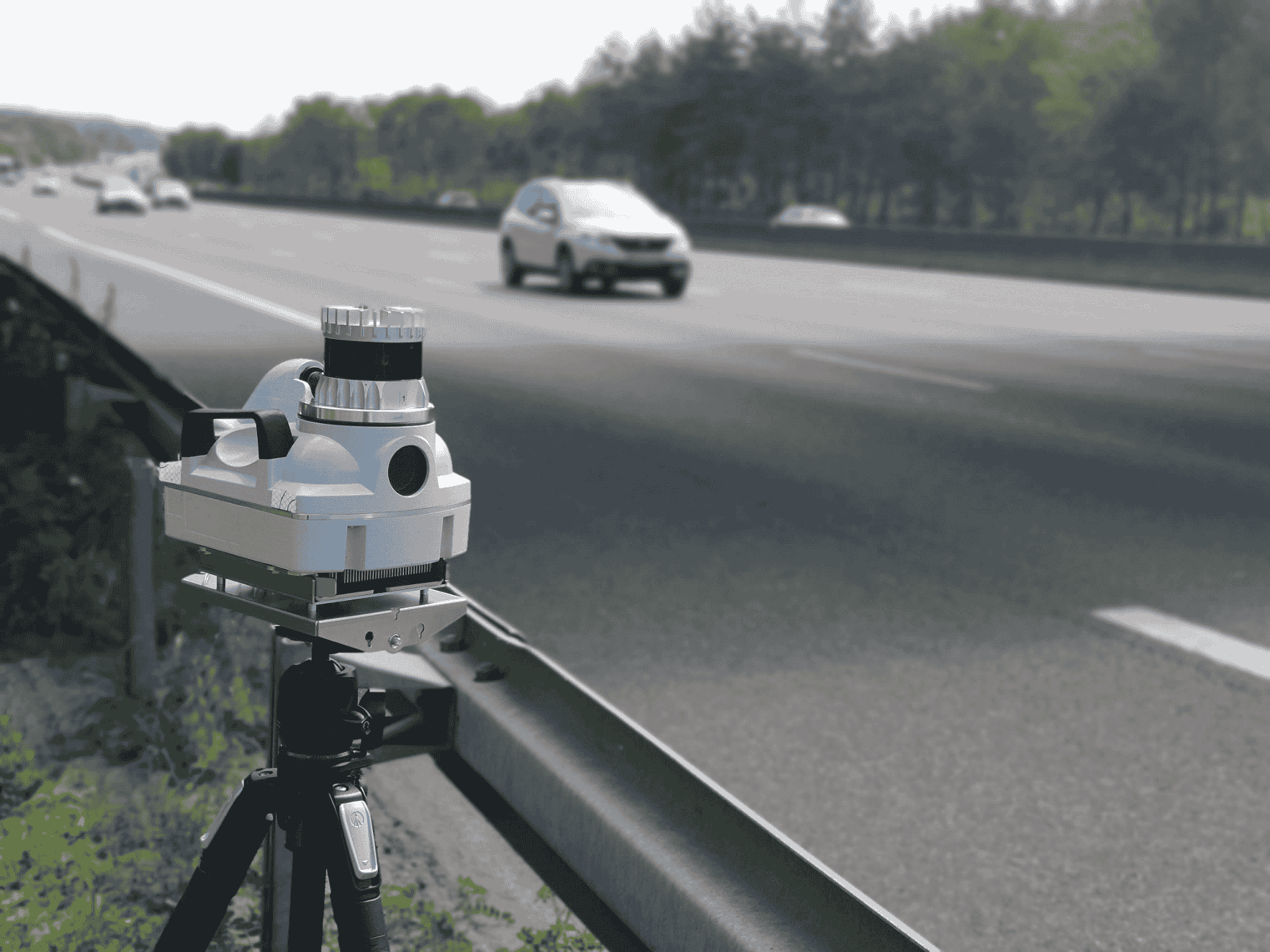
Law Enforcement and Security

- Speed Enforcement
Lidar devices are widely used to measure vehicle speed with high precision. - Traffic Monitoring
Agencies utilize Lidar to gather traffic flow data, detect congestion, and improve road safety strategies.
Use of Lidar in iPhones
Apple’s integration of Lidar into smartphones demonstrates its growing impact on consumer tech.
- Augmented Reality (AR)
Lidar enhances AR by providing accurate depth data, allowing digital objects to interact naturally with physical spaces. - Photography
Improved low-light autofocus and more accurate depth perception lead to sharper portraits and better imaging quality.
Urban Planning and Infrastructure Management
- City Mapping
Lidar supports detailed urban modeling—from buildings to utilities—helping cities optimize infrastructure planning. - Hazard Detection
Analyzing Lidar data helps identify vulnerabilities such as unstable ground or flood-prone zones.
Archaeology and Cultural Heritage
- Site Mapping
Lidar reveals structures hidden beneath vegetation or soil, enabling discoveries without excavation. - Artifact Preservation
Non-invasive mapping techniques help preserve delicate heritage sites while supporting research.
Conclusion
Lidar’s extensive applications—from autonomous systems to archaeological research—highlight its versatility and transformative potential. As technology evolves and sensor prices continue to fall, the adoption of Lidar is expected to grow even further. With companies like Coral Mountain supporting advanced data processing and AI integration, Lidar will continue unlocking new insights and pushing innovation across industries.
Recommended for you
- News
Explore how AVs learn to see: Key labeling techniques, QA workflows, and tools that ensure safe...
- News
How multi-annotator validation improves label accuracy, reduces bias, and helps build reliable AI training datasets at...
- News
Discover the world of point cloud object detection. Learn about techniques, challenges, and real-world applications. Introduction...
Coral Mountain Data
Office
- Group 3, Cua Lap, Duong To, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam
- (+84) 39 652 6078
- info@coralmountaindata.com
Data Factory
- An Thoi, Phu Quoc, Vietnam
- Vung Bau, Phu Quoc, Vietnam

Copyright © 2024 Coral Mountain Data. All rights reserved.