What does data annotation mean in Machine Learning? What types of annotation exist, and what methods are used? Let’s dive deeper.

Data labeling examples
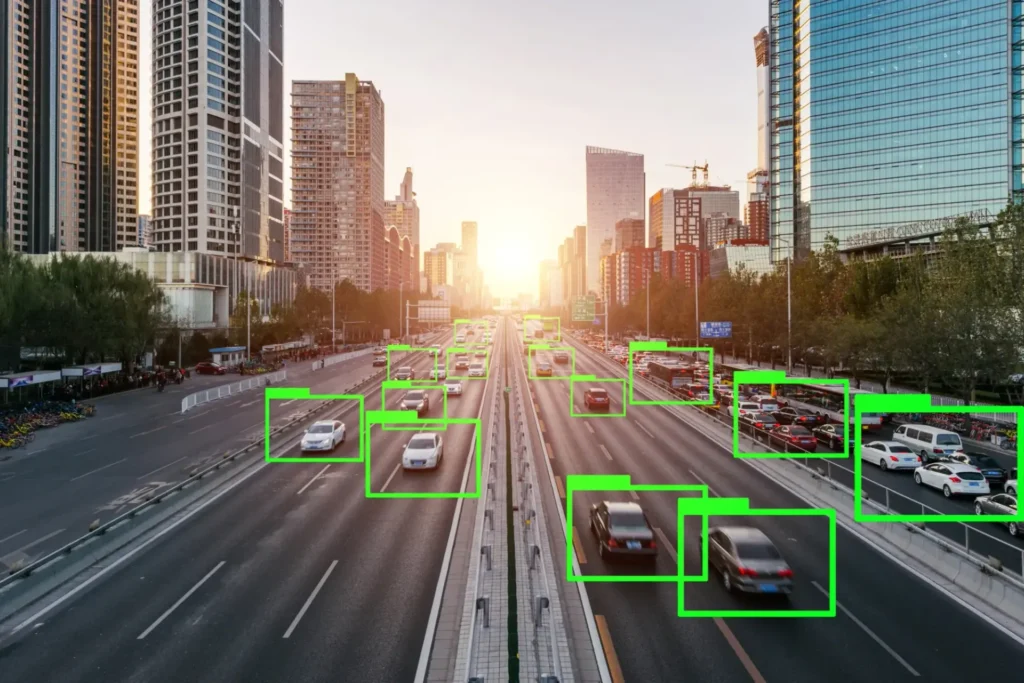
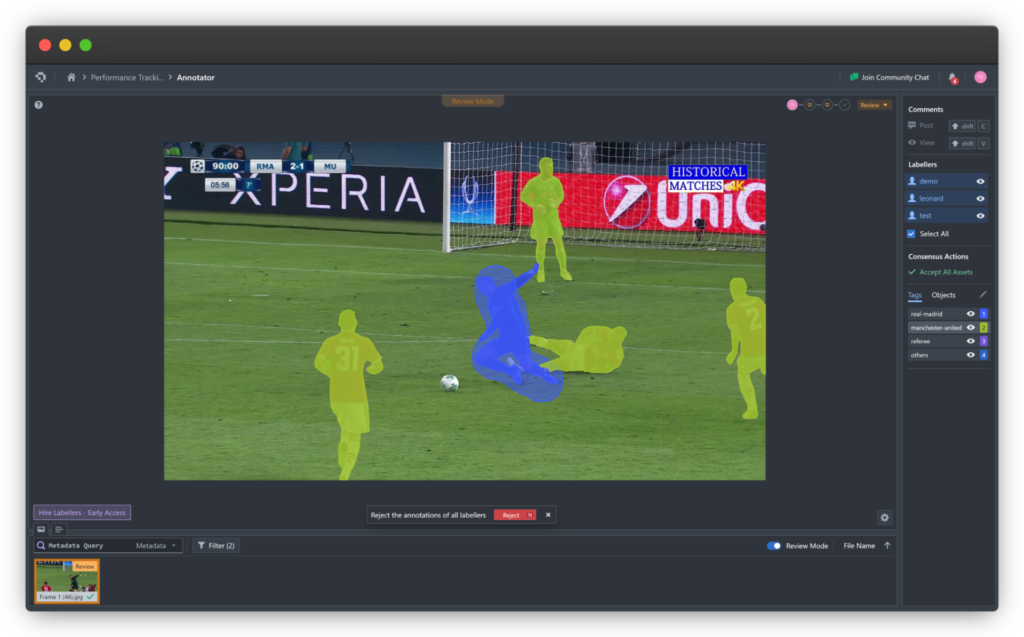
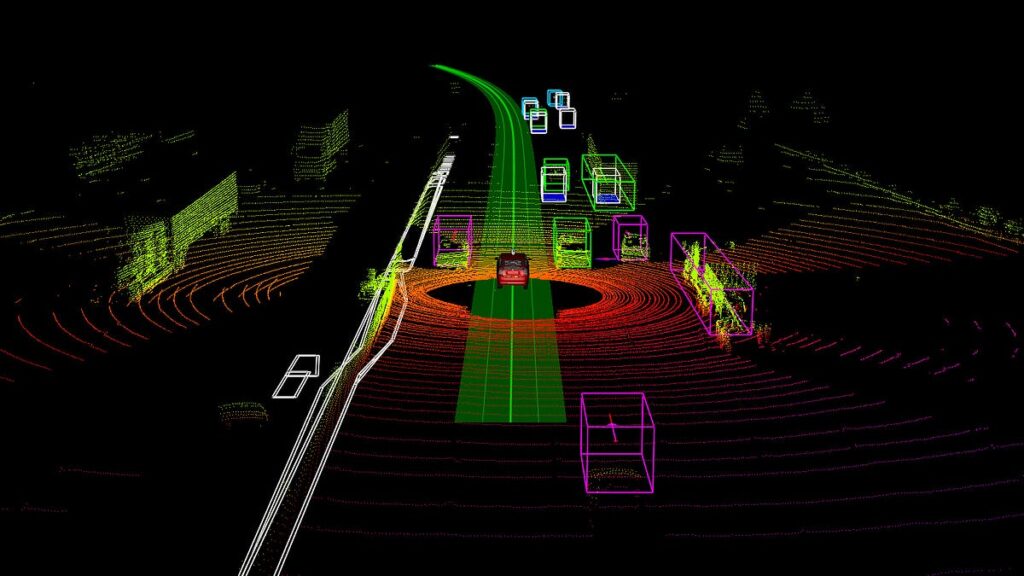
Three common applications of Data Annotation – Bounding Boxes, Semantic Segmentation, and 3D Point Cloud Tagging
AI and Machine Learning (ML) systems generally rely on two main elements: the algorithm and the data. The algorithm, often referred to as the ML model, dictates how data is processed and in what sequence. But the raw data that powers these models usually needs to be labeled, or annotated, before it can be used.
For example, if you want a system to recognize people in images, the model must first be trained on thousands of images where humans are clearly marked. This process—marking people within the images—is called Image Labeling. A dataset enriched with these annotations becomes the “Ground Truth,” the reference standard the model tries to learn from.
When a well-designed ML model is combined with high-quality ground truth data, the result is powerful applications like facial recognition, chatbots, speech recognition, recommendation engines, and more.
Why is data annotation needed?
Accurate annotation is at the core of successful AI systems. The challenge is the sheer speed at which new data is being generated. According to research by Visual Capitalist, by 2025, the world will produce an estimated 463 exabytes of data every single day.
ML engineers and data scientists spend much of their time cleaning and preparing this data—fixing errors, discarding unusable samples, and aligning formats. That’s why it’s invaluable to have annotation partners who can handle this preparation. Clean, well-labeled data prevents biases, reduces errors, and ensures algorithms detect patterns effectively—even in tricky edge cases.
Different types of Data Annotation
We can categorize annotation techniques based on the data format.
Image Labeling
Image annotation applies to both pictures and videos. It ensures that machines recognize selected regions as distinct objects. These areas may be marked using Bounding Boxes, Polygons, Cuboids, or Free-form boundaries.
Image labeling has wide-ranging applications—autonomous vehicles, robotic vision, medical AI, and retail automation. For instance:
- Medical AI: ML models trained on medical images can assist in diagnostics.
- Retail: Automated recognition of empty carts or catalog creation.
Automatic Image Annotation
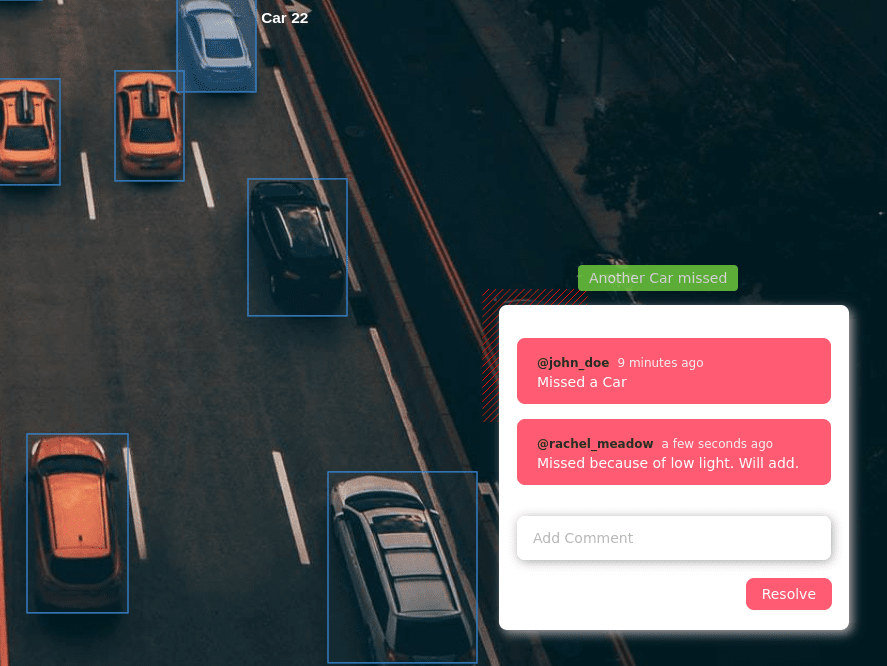
Traditionally, labeling images meant painstaking manual work. But with today’s massive data volumes, full manual annotation is impractical. Modern tools (like Mindkosh) now employ ML-based pre-labeling and interactive segmentation to speed things up. Emerging techniques like Active Learning push dataset performance even further.
Image Labeling Costs
Costs vary depending on the type and quality of annotation. At Mindkosh, our cost estimator tool lets you quickly approximate expenses based on your project’s scope. Generally, prices decrease in this order:
- Semantic Segmentation
- Object Detection (Bounding Box/Polygon)
- Object Detection (Polylines/Keypoints)
- Classification
For video and 3D data, pricing depends on annotation workload.
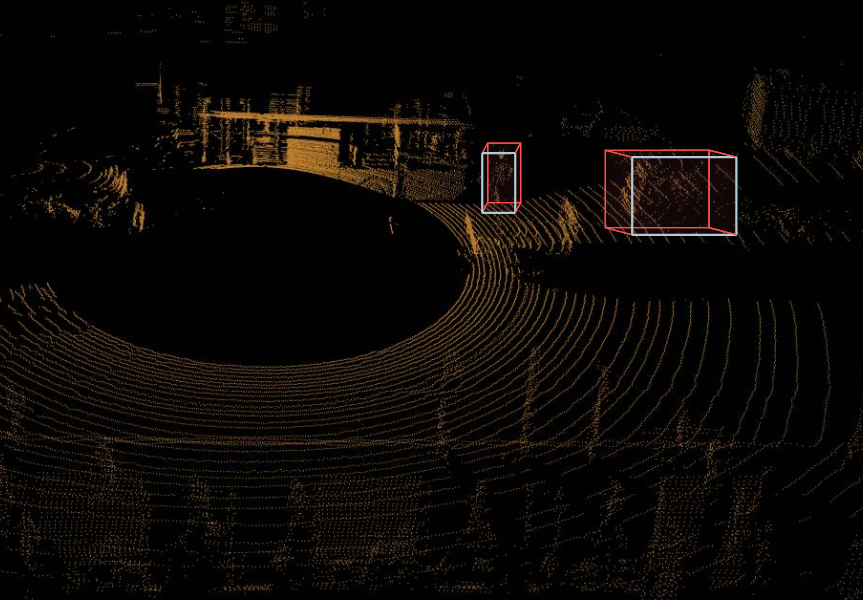
3D Point Cloud Annotation
3D point clouds are generated by LiDAR sensors to create a three-dimensional map of the environment. These datasets are essential in self-driving cars for localization, as well as in metrology and manufacturing for precision inspection.
Text Annotation
Since text is the most common form of data, text annotation covers a variety of tasks:
- Sentiment Annotation: Identifying attitudes, emotions, or opinions in text—useful in social media monitoring, though subjective and tricky.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Tagging words with categories like names, addresses, or places.
- Intent Annotation: Extracting user intent from text—important for chatbots, voice assistants, and booking systems.
- Text Categorization: Sorting documents or passages into topics (e.g., sports, politics, entertainment).
Audio Annotation
Audio data requires tasks like transcription, timestamping, and tagging speech characteristics—intonation, dialect, or emotional tone. It may also involve non-human sounds, such as alar
Coral Mountain Data is a company that provides high-quality data annotation services for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models, ensuring reliable input datasets. Our annotation solutions include LiDAR point cloud data, enhancing the performance of AI and ML models.
Recommended for you
- News
Explore how AVs learn to see: Key labeling techniques, QA workflows, and tools that ensure safe...
- News
How multi-annotator validation improves label accuracy, reduces bias, and helps build reliable AI training datasets at...
- News
Discover the world of point cloud object detection. Learn about techniques, challenges, and real-world applications. Introduction...
Coral Mountain Data
Office
- Group 3, Cua Lap, Duong To, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam
- (+84) 39 652 6078
- info@coralmountaindata.com
Data Factory
- An Thoi, Phu Quoc, Vietnam
- Vung Bau, Phu Quoc, Vietnam

Copyright © 2024 Coral Mountain Data. All rights reserved.