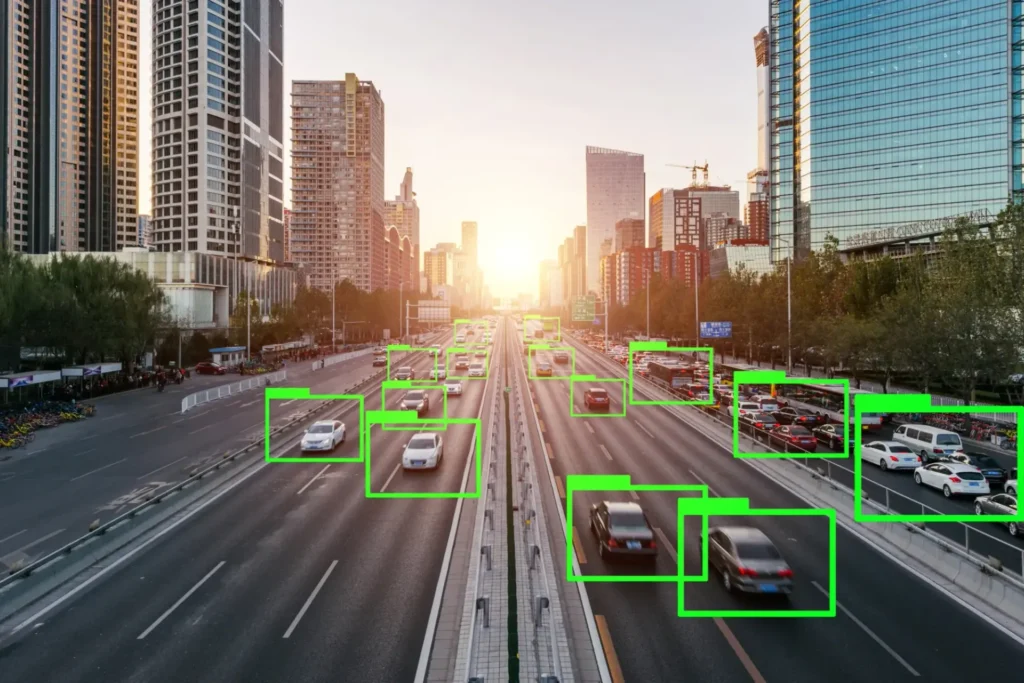
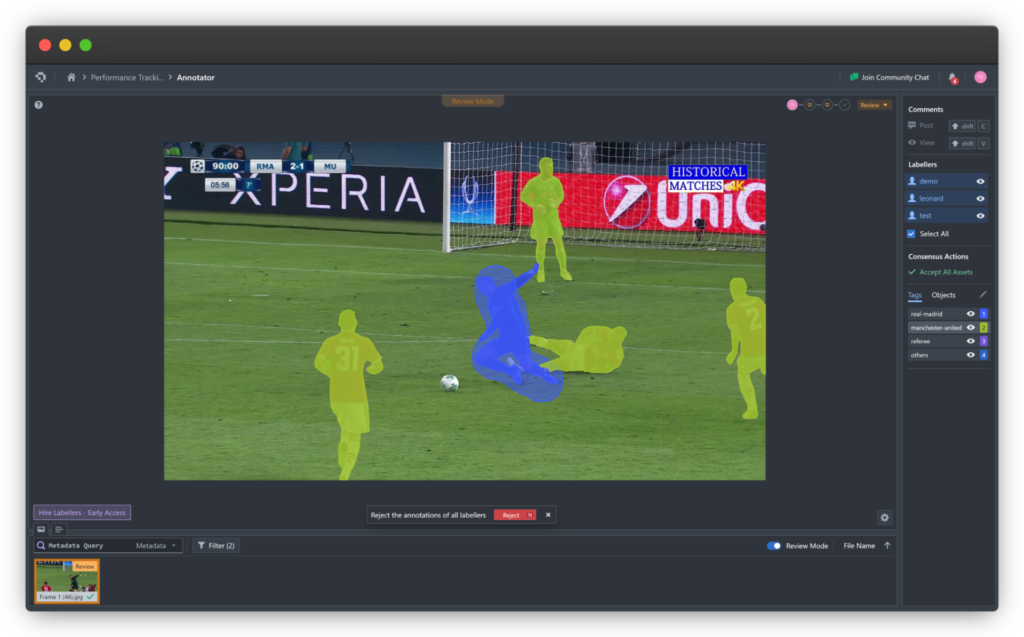
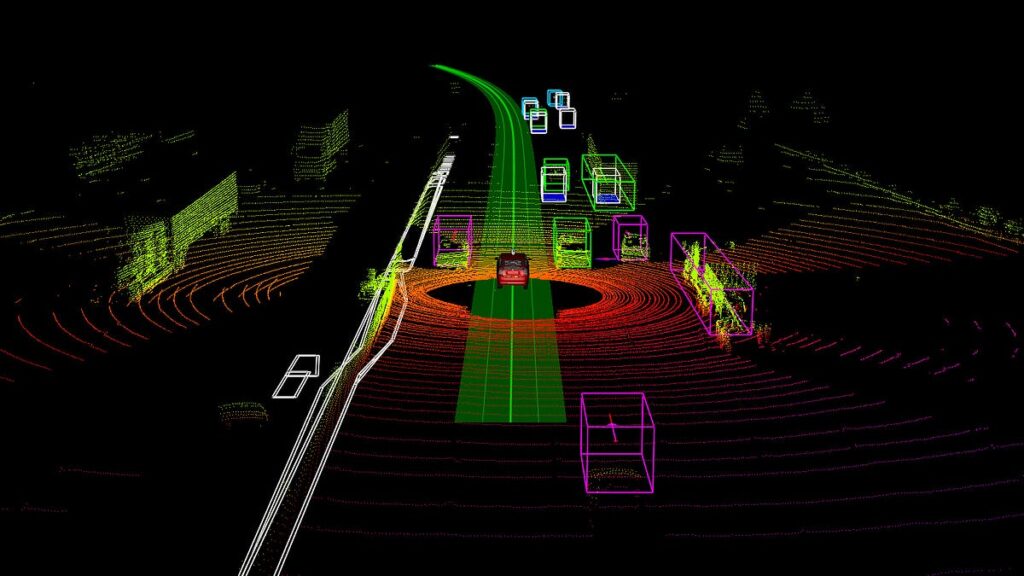
3D point clouds have become essential in fields such as robotics, autonomous vehicles, and forestry. Compared to traditional sensing technologies like cameras, point clouds offer significant advantages that make them highly suitable for industrial and scientific applications. In this article, we explore what a 3D point cloud is, how it is captured, common file formats and tools, and the many ways it is used across industries.
What is a 3D Point Cloud?
A point cloud is a digital 3D representation of an object or environment created from numerous individual data points. Each point is defined by three spatial coordinates — X, Y, and Z — which together approximate the shape and structure of the scanned object.
Beyond spatial coordinates, points may also include additional attributes such as RGB color values, intensity, or even temperature, depending on the scanning method used.
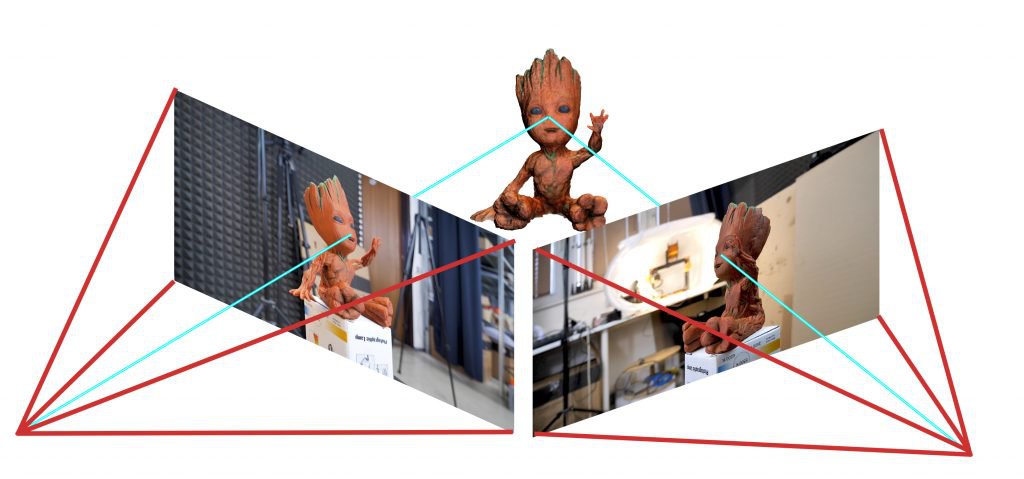
How is a Point Cloud Produced?
Point clouds are typically generated using advanced 3D scanning techniques.
LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
Uses laser pulses to measure distances by calculating the time taken for light to return to the sensor. Lidar is widely used in topographic mapping, forestry, and autonomous vehicles due to its accuracy over large environments.
RADAR (Radio Detection and Ranging)
Emits radio waves and measures the return time of reflected signals. Each reflection becomes a 3D data point, making radar useful in maritime navigation and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Photogrammetry
Combines multiple overlapping photographs taken from different angles to reconstruct a 3D structure. While less precise than lidar, it produces visually rich colorized point clouds and is popular in cultural heritage preservation and construction.
Structured Light Scanning
Projects a light pattern onto a surface and measures its deformation to infer 3D structure. Common in manufacturing and quality inspection.
Time-of-Flight Cameras
Measure the travel time of emitted light and are frequently used in robotics and gaming applications.
What Is a Point Cloud Scan?
A point cloud scan refers to the act of capturing 3D spatial data using technologies like lidar or photogrammetry. The resulting dataset — the actual collection of 3D points — is the point cloud itself.
Depending on the application, scanners may generate many point clouds per second, such as in autonomous vehicles where continuous real-time scanning is essential.
Common Point Cloud File Formats
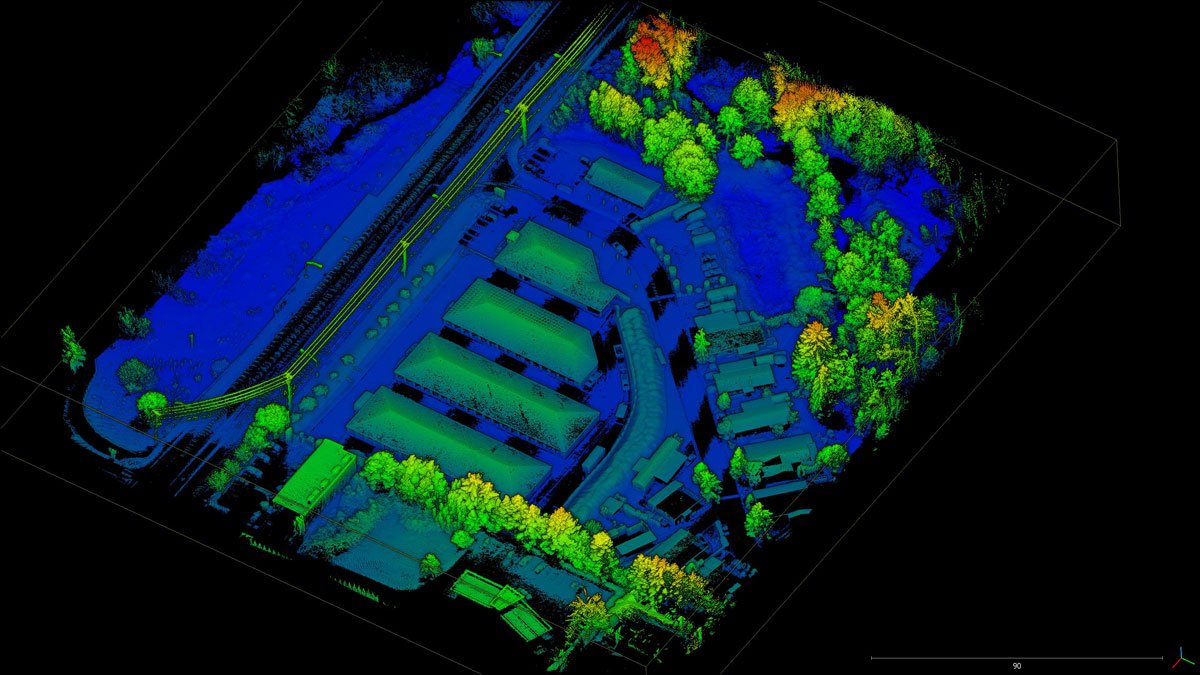

Some widely used formats include:
- PCD (Point Cloud Data): Frequently used for lidar-generated point clouds, available in ASCII and binary versions.
- PLY (Polygon File Format): Supports both point clouds and meshes, often used for object scans in medical and research applications.
- LAS: The standard format for aerial lidar scans from drones or aircraft. It supports additional metadata such as classification and RGB values.
Point Cloud Processing Software
Unlike images, point clouds require dedicated visualization and processing tools.
CloudCompare
A powerful open-source tool capable of handling large point clouds. It supports editing, segmentation, measurement, and even mesh processing.
MeshLab
Primarily used for mesh processing but also supports point cloud visualization, making it useful for 3D reconstruction tasks.
Point Cloud Annotation Tools
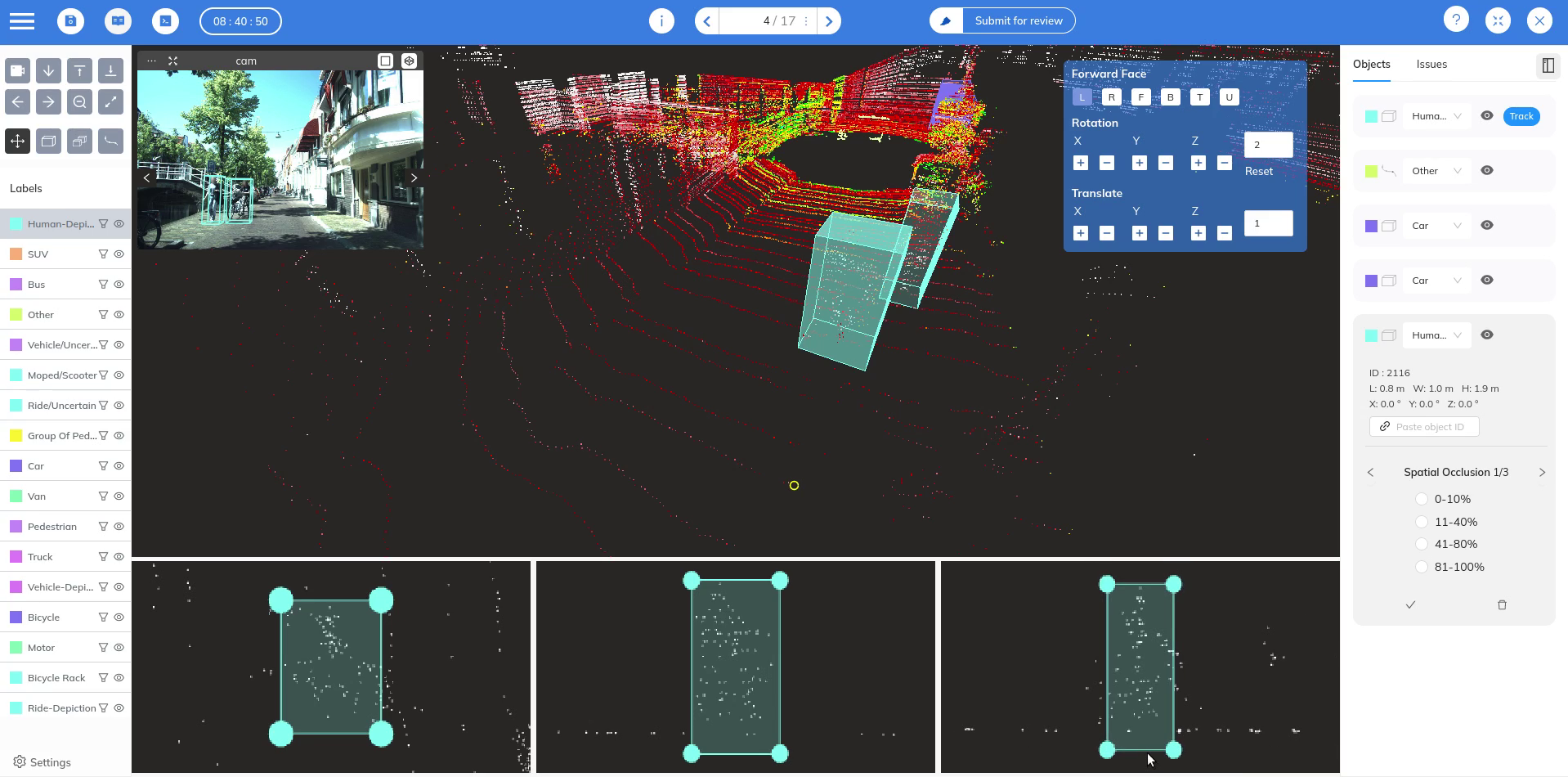
To train machine learning models on 3D data, point clouds must be annotated with semantic information. Coral Mountain offers a 3D point cloud annotation platform designed to handle both lidar data and synchronized camera imagery, allowing objects to be labeled consistently across multiple sensors and frames. It also supports dense colored point clouds with RGB data.
What Advantages Do Point Clouds Offer?
Point clouds provide several unique benefits:
- High spatial accuracy, allowing precise measurements and modeling.
- True 3D perception — unlike 2D images, point clouds capture depth and structure.
- Robustness in adverse weather conditions such as fog or rain, making them ideal for navigation and safety-critical applications.
Difference Between Depth Maps, Meshes, and Point Clouds
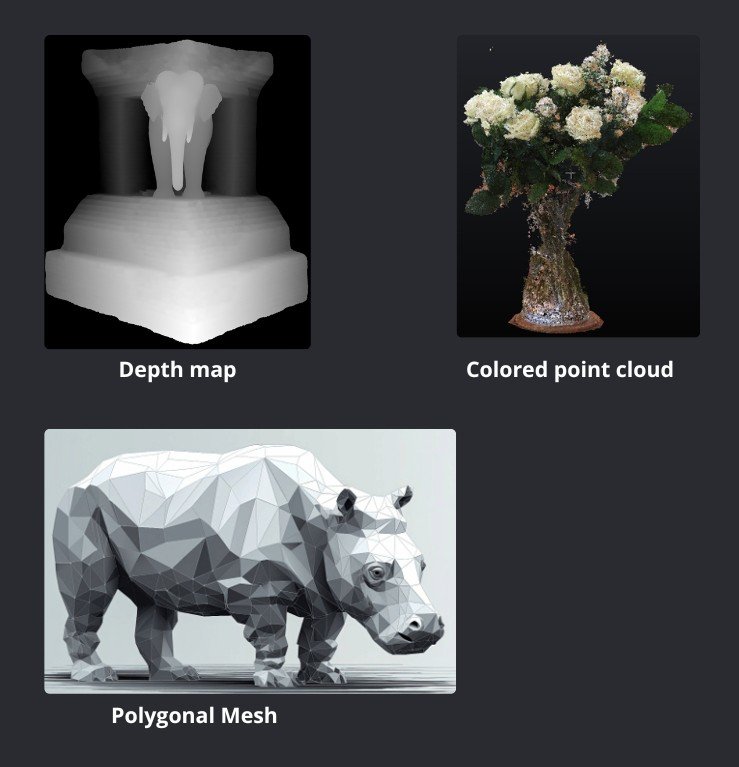

Depth Maps represent distance information in a 2D matrix format and are easy to process, but lack the accuracy and coverage of full point clouds.
3D Meshes connect points with faces to create continuous surfaces. They are ideal for rendering and simulation but require more processing to generate.
Point Clouds offer raw geometric precision and flexibility, making them more suitable for measurement and perception tasks.
Challenges of Using Point Clouds
Despite their advantages, point clouds come with certain challenges:
- Datasets can contain millions of points, requiring powerful hardware and optimized algorithms.
- Scan quality varies depending on the sensing method and environmental conditions.
- High-end scanners like lidar units are still relatively expensive and power-intensive, though costs are rapidly declining.
Industry Applications of Point Clouds
Point clouds are now used far beyond traditional surveying:
- Civil Engineering: For creating accurate 3D models of infrastructure.
- Agriculture: For field mapping and vegetation analysis.
- Mining: For deep-tunnel mapping without human risk.
- Drone Navigation: For precise obstacle detection and autonomous flight.
Conclusion
A 3D point cloud is one of the most powerful representations of spatial data available today. Captured through technologies like lidar and photogrammetry, point clouds enable detailed modeling and analysis of real-world environments. Their versatility makes them indispensable across industries ranging from construction and manufacturing to autonomy and virtual simulation. Mastering point cloud generation and processing opens the door to a new dimension of data intelligence.
Coral Mountain Data is a data annotation and data collection company that provides high-quality data annotation services for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models, ensuring reliable input datasets. Our annotation solutions include LiDAR point cloud data, enhancing the performance of AI and ML models. Coral Mountain Data provide high-quality data about coral reefs including sounds of coral reefs, marine life, waves….
Recommended for you
- News
Explore how AVs learn to see: Key labeling techniques, QA workflows, and tools that ensure safe...
- News
How multi-annotator validation improves label accuracy, reduces bias, and helps build reliable AI training datasets at...
- News
Discover the world of point cloud object detection. Learn about techniques, challenges, and real-world applications. Introduction...
Coral Mountain Data
Office
- Group 3, Cua Lap, Duong To, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam
- (+84) 39 652 6078
- info@coralmountaindata.com
Data Factory
- An Thoi, Phu Quoc, Vietnam
- Vung Bau, Phu Quoc, Vietnam

Copyright © 2024 Coral Mountain Data. All rights reserved.