What are Semantic and Instance segmentation techniques, and how do they differ from each other.
Instance vs Semantic Segmentation
Differences between Semantic and Instance segmentation techniques
Image segmentation is a fundamental task in computer vision, helping machines interpret visual information in a structured way. Among various techniques, semantic segmentation and instance segmentation are the two most commonly used approaches. Although they share similar goals, they operate at different levels of granularity and serve different purposes. This article provides a clear overview of both techniques, compares their capabilities, and highlights where each is most effective.
What is Semantic Segmentation?
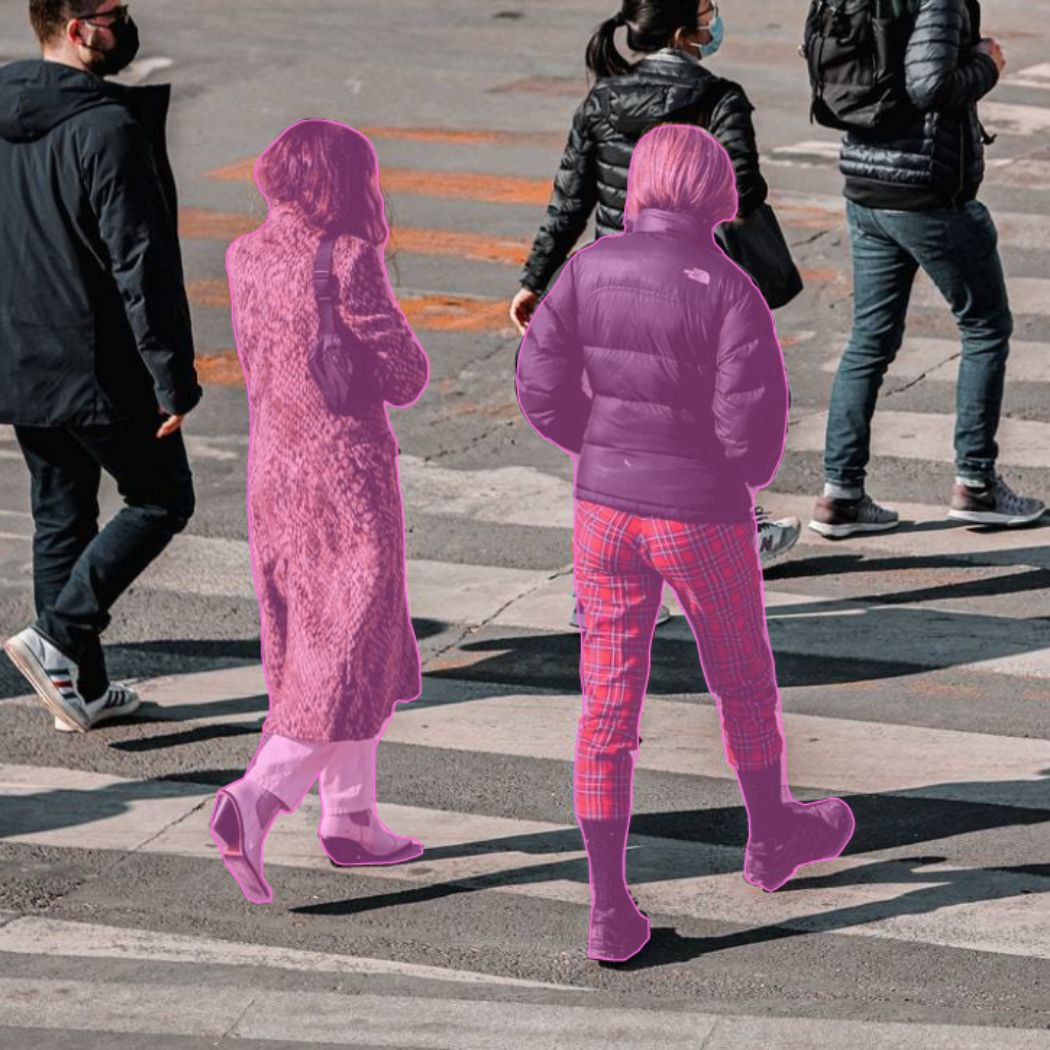

Semantic segmentation assigns a class label to every pixel in an image. Its goal is not to separate individual objects but to identify what categories are present and where they appear. For example, all pixels belonging to “cars” will be marked as car, all “trees” as tree, and so on—without distinguishing between one car and another.
This technique is widely used when scene understanding is more important than object individuality.
Key Characteristics
- Pixel-wise Labeling
Every pixel is classified into a predefined category, creating a full semantic map of the image. - Contextual Understanding
Semantic models use spatial and contextual cues to maintain consistency across regions. - Scene Parsing and Understanding
Useful for environmental analysis, urban mapping, and large-scale visual analytics. - Handling Class Ambiguity
Networks learn to distinguish between visually similar categories using context. - Applications Beyond Object Detection
Often used in image editing, background removal, and content-aware generation. - Computational Efficiency
With modern architectures, semantic segmentation can run in real time on edge devices. - Transfer Learning and Generalization
Pretrained models like DeepLab or U-Net can be fine-tuned for domain-specific tasks.
What is Instance Segmentation?
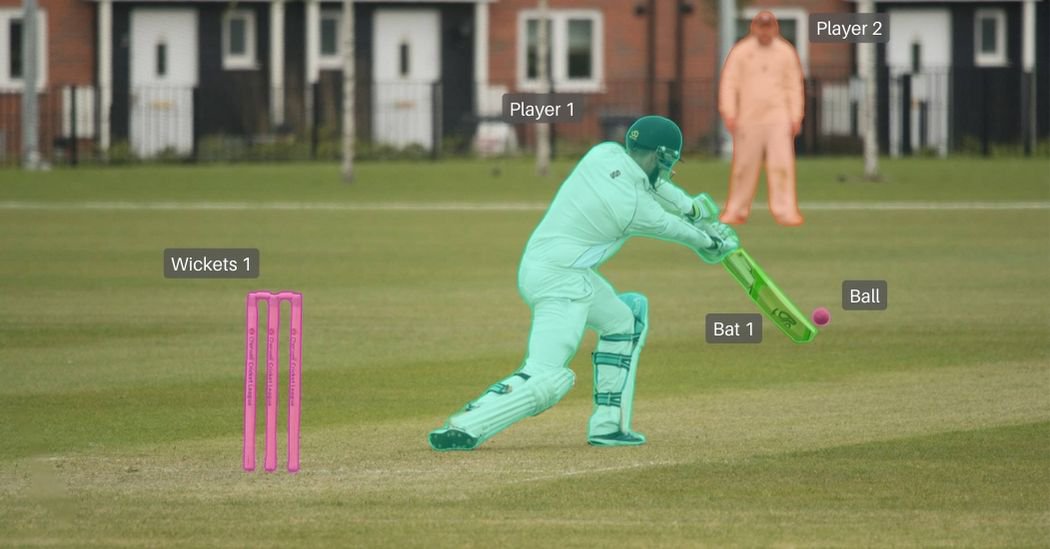

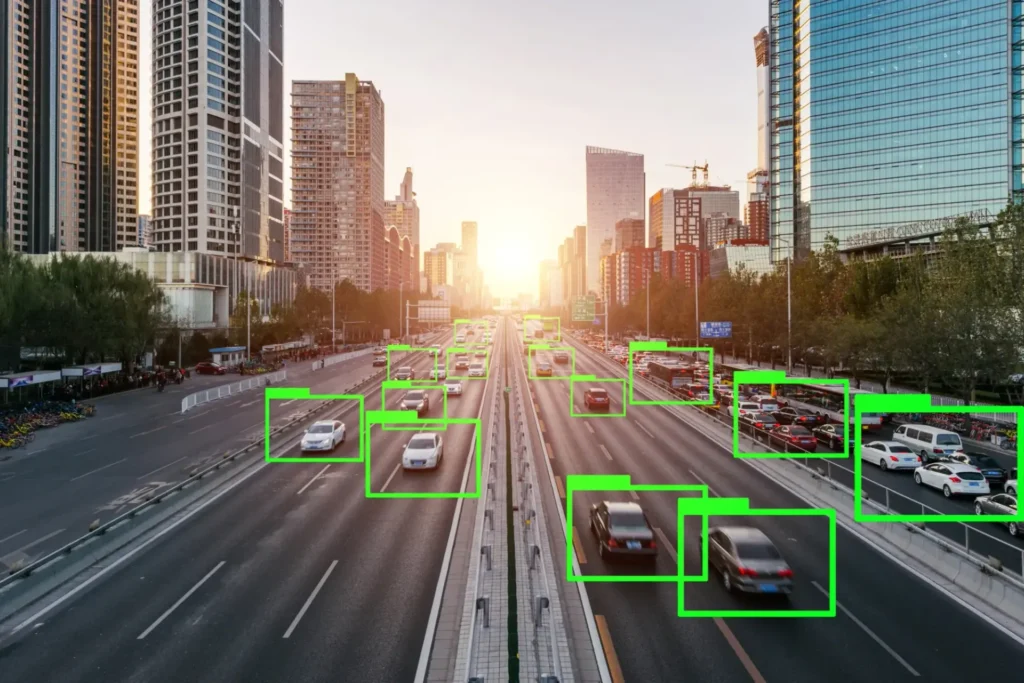
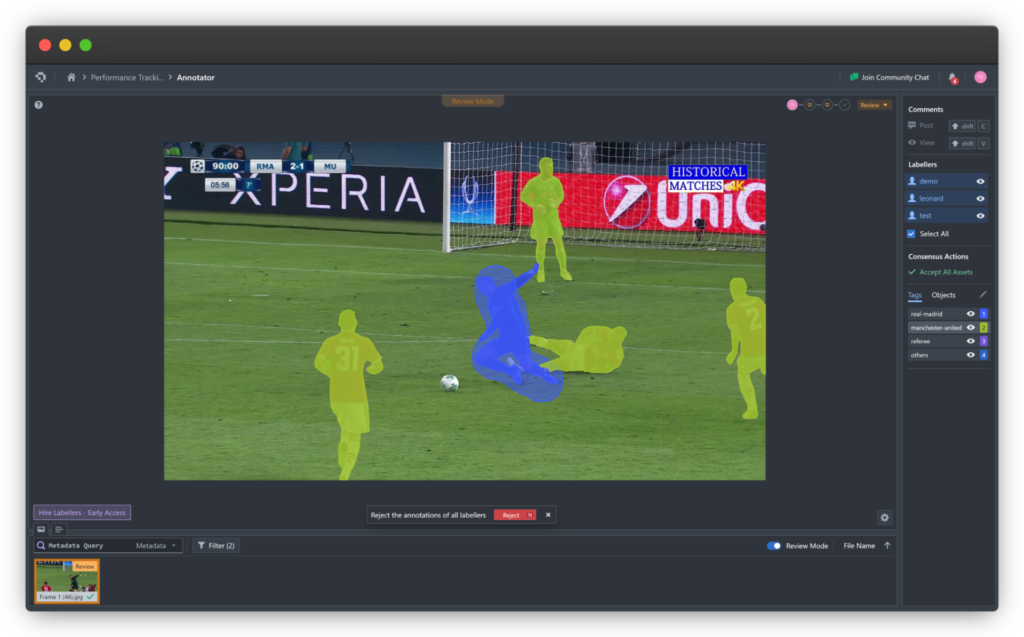
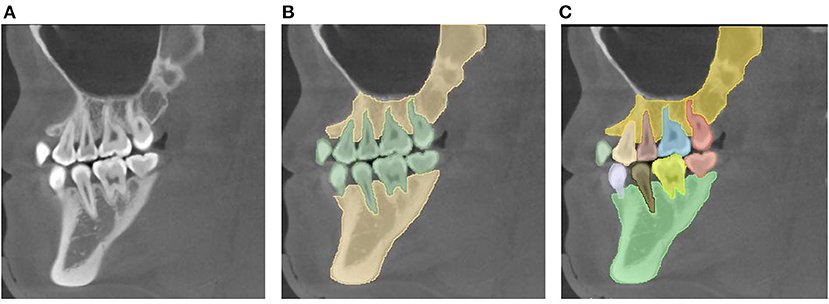
Instance segmentation builds upon semantic segmentation by not only identifying object classes but also separating individual objects within each class. If an image contains three cars, semantic segmentation marks them all as “car,” while instance segmentation creates three separate masks, one for each car.
This per-object separation enables deeper scene reasoning and object-level analytics.
Key Characteristics
- Precise Object Localization
Generates unique segmentation masks for each detected instance. - Handling Object Occlusion
Capable of detecting and segmenting objects even when partially blocked. - Semantic Understanding with Instance-level Detail
Provides more structured scene interpretation compared to pixel-classification alone. - Handling Object Size Disparities
Detects both small and large objects efficiently. - Seamless Integration with Object Detection
Often built on object detection frameworks like Mask R-CNN. - Scalability and Efficiency
Modern approaches balance accuracy and speed, enabling practical deployment. - Robustness to Class Imbalance
Uses techniques like instance-aware sampling to maintain accuracy across categories.
Difference Between Semantic and Instance Segmentation
The core difference lies in how each method treats individual objects.
- Semantic segmentation groups all objects of the same category into a single class.
- Instance segmentation identifies and separates each object individually, even within the same category.
Semantic segmentation is ideal for global scene understanding, while instance segmentation is better suited for object-level reasoning and interaction.
How It’s Done
Both techniques rely on deep learning, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
- Semantic segmentation commonly uses architectures like FCN or U-Net, which output a pixel-wise classification map.
- Instance segmentation typically uses frameworks like Mask R-CNN, which detect objects using bounding boxes and then generate individual masks.
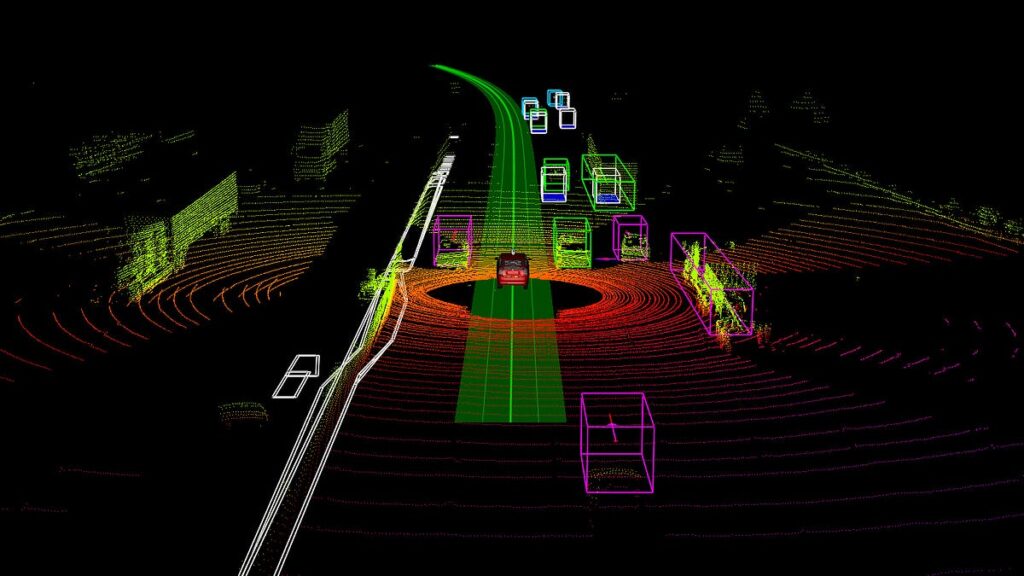
Use Cases for Instance Segmentation
- Autonomous Driving
Separates vehicles, pedestrians, and obstacles to enable safe navigation. - Medical Imaging
Helps in detecting and measuring individual tumors, organs, or anatomical structures.
Use Cases for Semantic Segmentation
- Scene Understanding
Used in satellite imagery analysis, environmental monitoring, and land classification. - Augmented Reality
Helps AR systems separate background from foreground for accurate overlay.
Annotation Challenges and Tooling
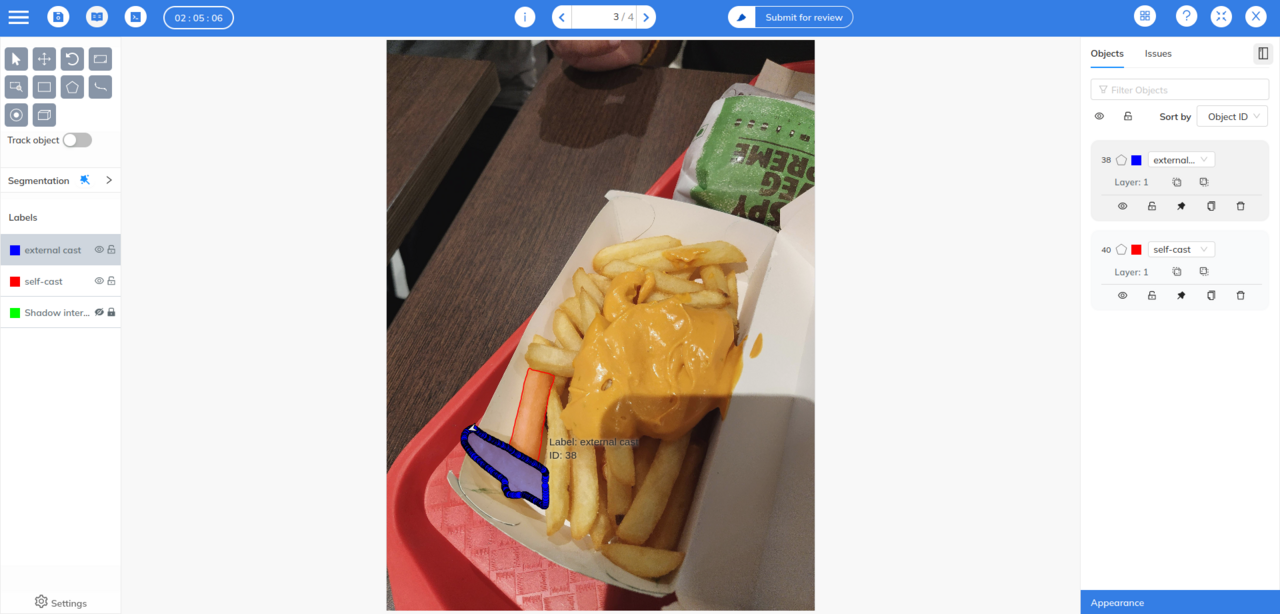
Both segmentation techniques demand precise pixel-level labeling, which can be labor-intensive. A well-designed annotation tool is crucial to simplify the process. Coral Mountain’s annotation platform supports both semantic and instance segmentation with features like:
- Multi-layer masking
- Quick previews
- Easy export formats
- AI-assisted tools such as “Magic Segment” for rapid selection
These tools significantly reduce manual effort and accelerate dataset creation.
Conclusion
Semantic and instance segmentation are both essential components of modern computer vision. While semantic segmentation offers a high-level understanding of scene composition, instance segmentation provides detailed per-object distinction. The choice between them depends on whether category-level insight or object-level precision is required.
With advances in deep learning and annotation tooling from platforms like Coral Mountain, both approaches are now more accessible than ever—powering applications from autonomous driving to healthcare and beyond.
Coral Mountain Data is a data annotation and data collection company that provides high-quality data annotation services for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models, ensuring reliable input datasets. Our annotation solutions include LiDAR point cloud data, enhancing the performance of AI and ML models. Coral Mountain Data provide high-quality data about coral reefs including sounds of coral reefs, marine life, waves….
Recommended for you
- News
Explore how AVs learn to see: Key labeling techniques, QA workflows, and tools that ensure safe...
- News
How multi-annotator validation improves label accuracy, reduces bias, and helps build reliable AI training datasets at...
- News
Discover the world of point cloud object detection. Learn about techniques, challenges, and real-world applications. Introduction...
Coral Mountain Data
Office
- Group 3, Cua Lap, Duong To, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam
- (+84) 39 652 6078
- info@coralmountaindata.com
Data Factory
- An Thoi, Phu Quoc, Vietnam
- Vung Bau, Phu Quoc, Vietnam

Copyright © 2024 Coral Mountain Data. All rights reserved.