How multi-annotator validation improves label accuracy, reduces bias, and helps build reliable AI training datasets at scale
In the field of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI), the principle of “garbage in, garbage out” remains highly relevant. Model performance is directly dependent on the quality of the data used during training, and accurate labeling is one of the most critical components of high-quality datasets. However, because human annotators naturally bring subjectivity into the process, inconsistencies and bias can easily be introduced. This challenge is precisely where multi-annotator validation proves its value.
Multi-annotator validation involves assigning the same data samples to multiple annotators and aggregating their labels to reach a more reliable and unbiased consensus. This approach is particularly important in complex and high-risk domains such as Healthcare, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Autonomous Driving, where even small labeling errors can result in significant downstream consequences for model behavior and safety.

Core Concepts
Majority voting
Majority voting is the most straightforward method for deriving consensus among multiple annotators. In this approach, the label selected by the largest number of annotators becomes the final assigned label.
Pros:
- Simple and easy to implement
- Effective when annotators have comparable expertise
Cons:
- Does not account for differences in annotator reliability
- Struggles with ambiguous or subjective cases
While majority voting works well in many scenarios, it can fall short when annotation tasks are complex or when annotator skill levels vary significantly.
Label aggregation techniques
To overcome the limitations of simple voting, more advanced aggregation methods incorporate annotator reliability and uncertainty into the labeling process. Common approaches include:
- Bayesian Models, which estimate the probability of each label being correct based on annotator performance
- Dawid-Skene Algorithm, which assigns different weights to annotators according to their historical accuracy
- Probabilistic Fusion Methods, which combine labels while explicitly modeling uncertainty
These techniques are especially valuable in domains such as medical imaging and autonomous vehicle perception, where precision is non-negotiable.
Inter-annotator agreement
Evaluating how consistently annotators label the same data points is a key indicator of annotation quality. Commonly used agreement metrics include:
- Cohen’s Kappa, which measures agreement between two annotators while correcting for chance
- Fleiss’ Kappa, which extends this concept to multiple annotators
- Krippendorff’s Alpha, which supports multiple annotators, missing data, and different data types
High agreement scores suggest reliable annotations, while low scores often indicate unclear guidelines or the need for additional annotator training. These inter-annotator agreement techniques are explored in greater depth in our dedicated resources.
Annotator expertise and bias
Annotation quality can vary due to differences in experience, fatigue, or cognitive bias. Several strategies help mitigate these risks:
- Weighting annotations so that inputs from more experienced annotators carry greater influence
- Monitoring label confusion trends to detect systematic mislabeling patterns
- Rotating tasks to reduce fatigue and prevent overfamiliarity with specific data types
Proactively managing annotator performance is essential for maintaining long-term dataset quality.
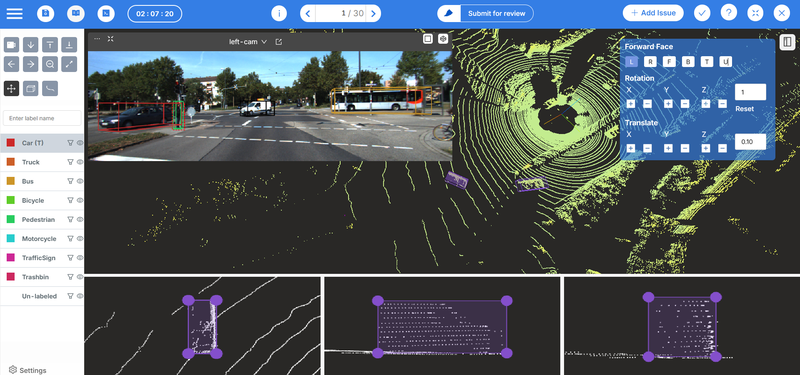
Choosing the right annotation tool
Discover how much your data annotation project might cost with our easy-to-use cost estimator. Visit our cost estimator page today and get a quick and accurate estimate tailored to your needs.
In practice, maintaining accuracy, consistency, and accountability across multiple annotators can quickly become challenging. Different interpretations of the same data are inevitable, and without the right tooling, teams risk losing context, introducing errors, or slowing down quality assurance workflows.
Choosing the right annotation platform is therefore critical. A robust tool must support collaboration while ensuring strong version control and traceability. Coral Mountain’s annotation platform is designed specifically to address these challenges in large-scale, multi-annotator environments.
The platform allows project managers to assign the same tasks to multiple annotators while keeping each contributor’s work isolated and fully traceable. Each annotation version is preserved independently, making it easy to compare outputs, analyze discrepancies, and understand how different annotators approached the same data.
Once annotation is complete, QA specialists can review all submitted versions and select the one that best meets quality standards. This selected version is then finalized as ground truth. This workflow enhances transparency, improves label accuracy, and significantly accelerates review cycles—making Coral Mountain well suited for complex, collaborative annotation projects.
More advanced topics
Annotator confusion matrices
Confusion matrices provide valuable insight into patterns where annotators repeatedly confuse specific labels. This analysis can:
- Reveal areas where annotation guidelines require clarification
- Identify annotators who may need additional training
- Feed into AI-driven scoring systems for annotator performance evaluation
Ground truth estimation
In situations where a definitive ground truth does not exist, consensus labeling acts as a practical substitute. Common methods include:
- Expectation-Maximization (EM) to iteratively estimate the most probable true labels
- Weighted Voting, which accounts for annotator reliability
- Gold-Standard Verification, where consensus labels are compared against a subset of expert-labeled data
Label noise and uncertainty
Noisy labels can significantly degrade model performance. Several strategies help mitigate this issue:
- Label Smoothing, which prevents overconfident predictions by softening hard labels
- Reweighting, which reduces the influence of ambiguous samples during training
- Uncertainty-aware Learning, which explicitly incorporates label uncertainty into model optimization
Annotation process optimization
Optimizing the annotation pipeline can substantially improve both efficiency and label quality. Key best practices include:
- Clear Instructions, with detailed guidelines to minimize ambiguity
- Thoughtful UI Design, enabling efficient quality control, communication, and task management
- Feedback Mechanisms, allowing annotators to flag uncertain cases or suggest guideline improvements
You can explore how Coral Mountain’s annotation tool supports these capabilities and more through our platform overview.
Practical applications

Crowdsourcing and annotation networks
Crowdsourcing platforms such as Amazon Mechanical Turk scale annotation efforts by:
- Assigning the same tasks to multiple annotators
- Aggregating results using consensus algorithms
- Applying quality control checks to improve reliability
Large datasets like ImageNet and Open Images have successfully used these techniques. However, while crowdsourcing offers cost advantages, the lack of structured oversight often results in inconsistent label quality. Multi-annotator setups can improve accuracy but may also increase costs, reducing the economic benefits of crowdsourcing. You can review pricing for Coral Mountain’s fully managed annotation services to explore alternatives.
Creating golden datasets and choosing annotators
Multi-annotator validation is particularly valuable for building “golden” datasets with exceptionally high-quality labels. These datasets can serve as reference standards to train new annotators or to evaluate ongoing labeling quality through methods such as honeypots.
Selecting the right annotator team is equally important, especially for tasks that require domain expertise or involve inherent ambiguity. In areas such as NLP and LLM-related tasks, multi-annotator setups are often the only reliable way to capture nuanced interpretations and ensure high-quality labeling.
Conclusion
Multi-annotator validation is not merely a quality control step—it is a foundational element of trustworthy machine learning pipelines. By leveraging consensus mechanisms, measuring inter-annotator agreement, and continuously refining annotation workflows, organizations can significantly improve dataset accuracy and consistency.
As AI systems are increasingly deployed in critical, real-world applications, the importance of high-quality labeled data continues to grow. Implementing robust multi-annotator validation strategies ensures that models are trained on data that genuinely reflects real-world complexity, resulting in more reliable, transparent, and effective AI solutions.
Coral Mountain Data is a data annotation and data collection company that provides high-quality data annotation services for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models, ensuring reliable input datasets. Our annotation solutions include LiDAR point cloud data, enhancing the performance of AI and ML models. Coral Mountain Data provide high-quality data about coral reefs including sounds of coral reefs, marine life, waves….
Recommended for you
- News
Explore how AVs learn to see: Key labeling techniques, QA workflows, and tools that ensure safe...
- News
Discover the world of point cloud object detection. Learn about techniques, challenges, and real-world applications. Introduction...
- News
Understand how far Lidar sensors can detect and the factors that influence their range, including sensor...
Coral Mountain Data
Office
- Group 3, Cua Lap, Duong To, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam
- (+84) 39 652 6078
- info@coralmountaindata.com
Data Factory
- An Thoi, Phu Quoc, Vietnam
- Vung Bau, Phu Quoc, Vietnam

Copyright © 2024 Coral Mountain Data. All rights reserved.