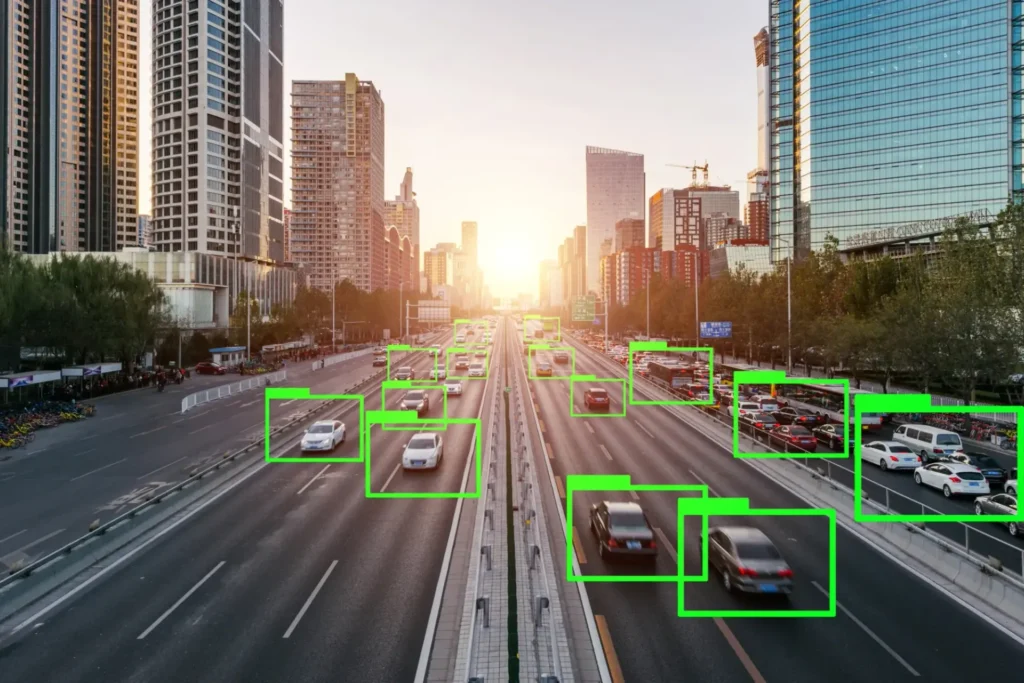
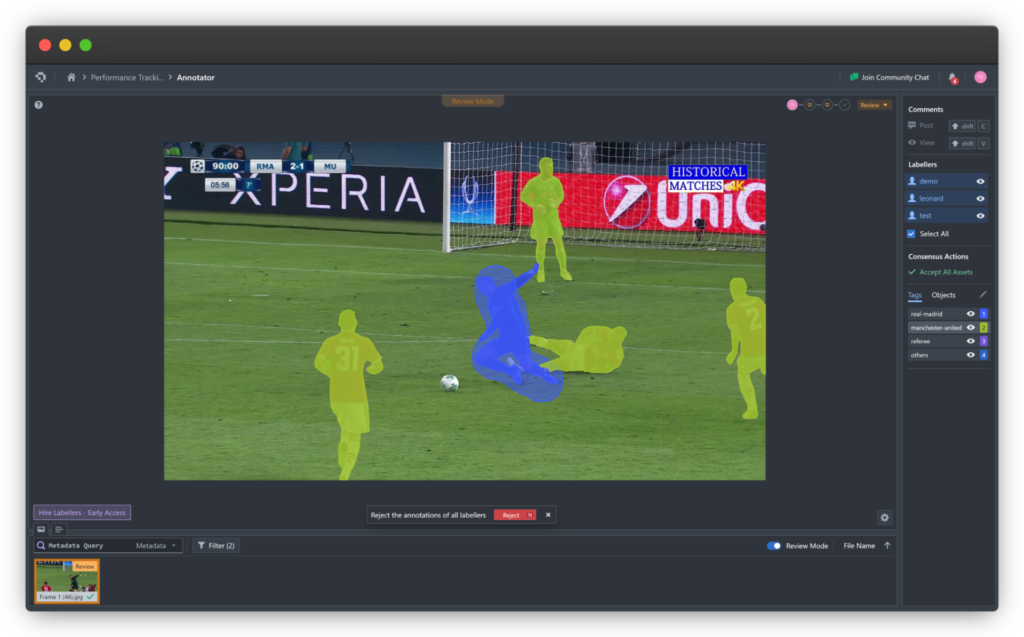
Compared to bounding boxes, polygons enable far more precise object detection. In this article, we explore polygon annotation — its advantages, tools, use cases, and why it’s a critical component of accurate computer vision systems.
Giới Thiệu
Are you facing challenges with the limitations of bounding boxes in your Machine Learning or Computer Vision projects? Whether it’s identifying the detailed contours of vehicles in autonomous driving or isolating irregularly shaped tumors in medical scans, bounding boxes often fail to capture fine details accurately.
Polygon annotation offers a powerful alternative by outlining objects with high fidelity to their real-world shapes. In this article, we’ll discuss how polygon annotation works, why it outperforms traditional methods, and how it can dramatically improve the accuracy and reliability of your models.
What is Polygon Annotation?
Polygon annotation involves marking the exact outlines of objects within an image using a series of connected points to form a closed polygon. Unlike bounding boxes — which are limited to rectangular shapes — polygons can have an unlimited number of vertices, allowing them to fit complex and irregular shapes precisely.
This flexibility makes polygon annotation indispensable for datasets where precision is critical, such as in autonomous vehicles, geospatial analysis, and medical imaging.
Advantages of Polygon Annotation

When labeling with bounding boxes, significant portions of the background are often included, introducing noise and reducing model accuracy. Polygon annotation solves this problem by tracing the actual boundaries of objects, enabling more refined datasets and improved learning outcomes.
1. Enhanced Precision
Polygon annotations conform tightly to the contours of the object, minimizing background inclusion and improving segmentation accuracy.
- Accurate Representation: Captures the object’s true shape and edges.
- Reduced Background Noise: Eliminates irrelevant pixels that can degrade training results.
This precision is particularly valuable for objects with complex geometries — such as animals, vehicles, or natural features in aerial imagery.
2. Improved Augmentation Performance
During data augmentation (rotations, translations, and scaling), bounding boxes can distort or lose alignment. Polygons, however, maintain their shape and relative structure, ensuring consistent data quality throughout transformations.
- Shape Integrity: Polygons preserve object outlines even under transformations.
- Data Consistency: Enhances the robustness and generalization ability of ML models.
3. Superior Object Localization
Polygon annotation provides exact object boundaries, enabling pixel-level accuracy. This is critical in use cases where small misclassifications can have serious consequences.
- Precise Localization: Essential for safety-critical systems like self-driving vehicles and surgical imaging.
- Ideal for Complex Shapes: Perfect for irregular or organic forms.
4. Versatility in Applications
Beyond simple detection, polygon annotations can be used in instance segmentation, semantic segmentation, or even rotated bounding box tasks. This adaptability makes them valuable for multiple deep learning model architectures and research workflows.
- Multi-purpose Use: Suitable for object detection, segmentation, and orientation-based labeling.
- Experimental Flexibility: Supports a wide range of model architectures and training objectives.
ML Models for Polygon Detection
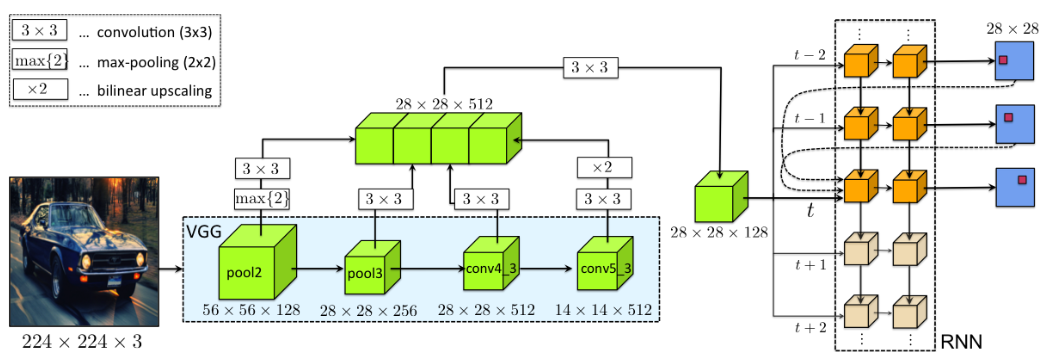
Recent years have seen significant advancements in polygon-based object detection models. While Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) remain the backbone of these systems, specialized architectures like Mask R-CNN and Polygon-RNN++ have become the industry standard.
Polygon-RNN++
Unlike segmentation models such as Mask R-CNN that output pixel masks, Polygon-RNN++ directly predicts polygon vertices iteratively, refining them step by step for improved accuracy. This iterative approach enables it to capture fine details — ideal for aerial, satellite, and architectural datasets where precision is crucial.
Use Cases for Polygon Annotation
1. Geospatial Data
In satellite and drone imagery, polygons are essential for annotating irregular land areas, forests, buildings, and water bodies.
- Detailed Mapping: Defines precise contours of natural or man-made structures.
- Improved Analysis: Leads to better geospatial segmentation and land-use classification.
2. Autonomous Driving
Self-driving vehicles require exact identification of pedestrians, vehicles, lanes, and obstacles. Polygon annotation enhances detection accuracy, supporting safer navigation.
- Complex Shape Detection: Handles the variability of real-world scenes.
- Safety Assurance: Critical for high-stakes autonomous systems.
3. Medical Imaging
In medical datasets, accuracy can be life-saving. Polygon annotations help delineate tumors, organs, or other irregular structures for diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Precise Segmentation: Outlines complex biological forms.
- Enhanced Diagnostic Reliability: Improves detection accuracy for medical AI models.
Implementation Strategies
Annotation Tools for Polygon Labeling
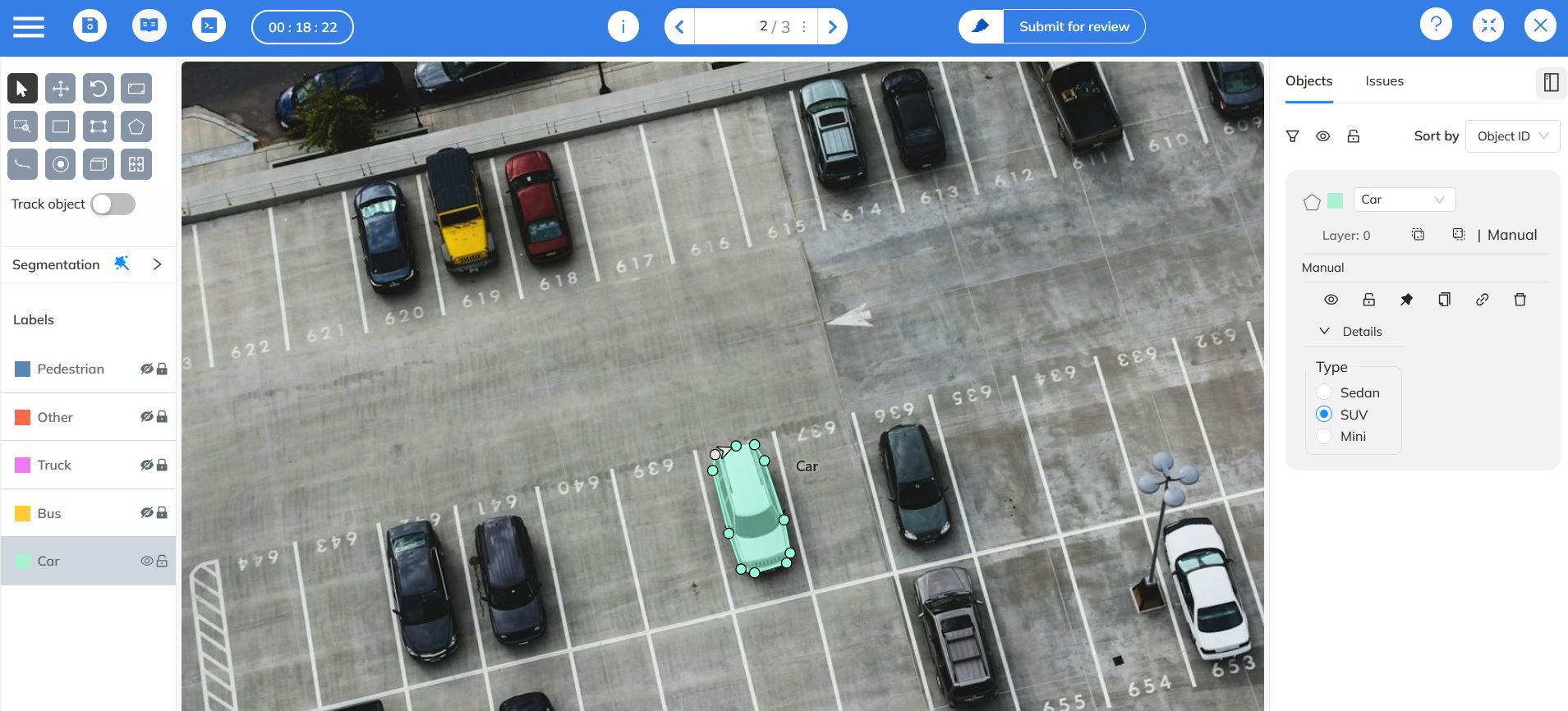
Not all data annotation platforms support polygon labeling effectively. When choosing a tool, it’s essential to ensure:
- Efficient Polygon Editing: Features like adjustable vertices, vertex snapping, and shape manipulation.
- Collaboration Capabilities: Real-time teamwork between annotators, quality controllers, and project managers.
- Built-in Quality Control: Automated review systems and detailed quality reports to maintain consistency.
- Flexible Export Options: Support for formats like COCO, Pascal VOC, or custom polygon data structures.
At Coral Mountain, our polygon annotation interface is designed for scalability and precision. With built-in collaboration, QC pipelines, and export compatibility, it simplifies the process of creating large, high-quality polygon-labeled datasets — reducing manual effort while maximizing accuracy.
Conclusion
Polygon annotation represents a leap forward in computer vision precision. Though it demands more time and expertise, its benefits — from improved model accuracy to better data integrity — make it indispensable for modern AI pipelines.
By integrating advanced annotation tools like those from Coral Mountain, your team can efficiently produce pixel-perfect datasets that power robust, high-performing Machine Learning models.
Coral Mountain Data is a data annotation and data collection company that provides high-quality data annotation services for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models, ensuring reliable input datasets. Our annotation solutions include LiDAR point cloud data, enhancing the performance of AI and ML models. Coral Mountain Data provide high-quality data about coral reefs including sounds of coral reefs, marine life, waves….
Recommended for you
- News
Most remote work today faces the same underlying economic pressure: commoditization driven by automation and global...
- News
Explore how AVs learn to see: Key labeling techniques, QA workflows, and tools that ensure safe...
- News
How multi-annotator validation improves label accuracy, reduces bias, and helps build reliable AI training datasets at...
Coral Mountain Data
Office
- Group 3, Cua Lap, Duong To, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam
- (+84) 39 652 6078
- info@coralmountaindata.com
Data Factory
- An Thoi, Phu Quoc, Vietnam
- Vung Bau, Phu Quoc, Vietnam

Copyright © 2024 Coral Mountain Data. All rights reserved.