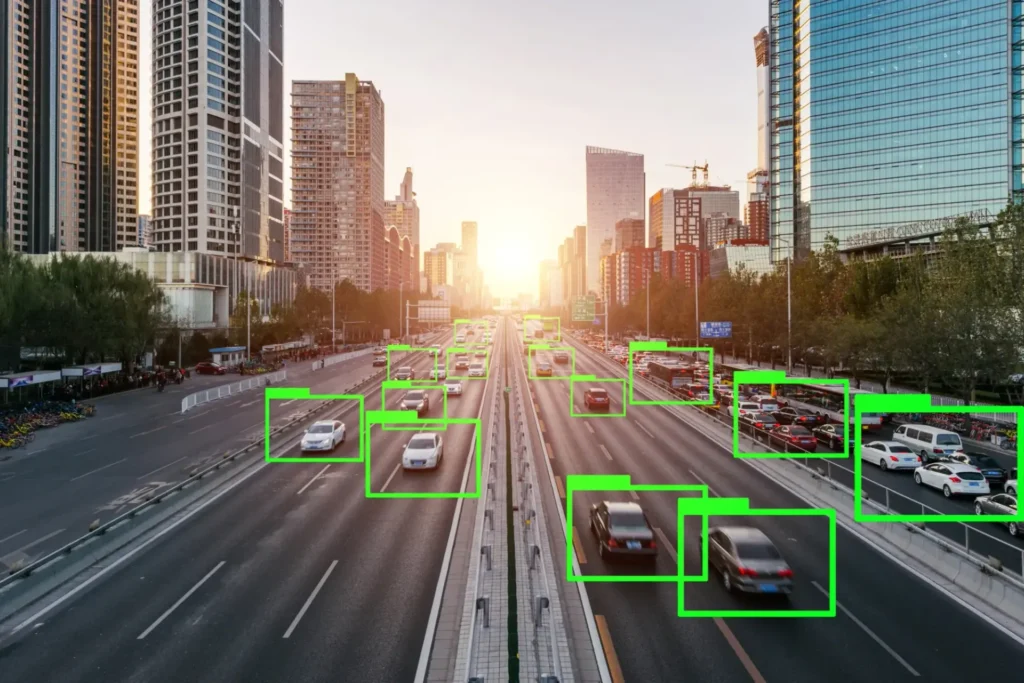
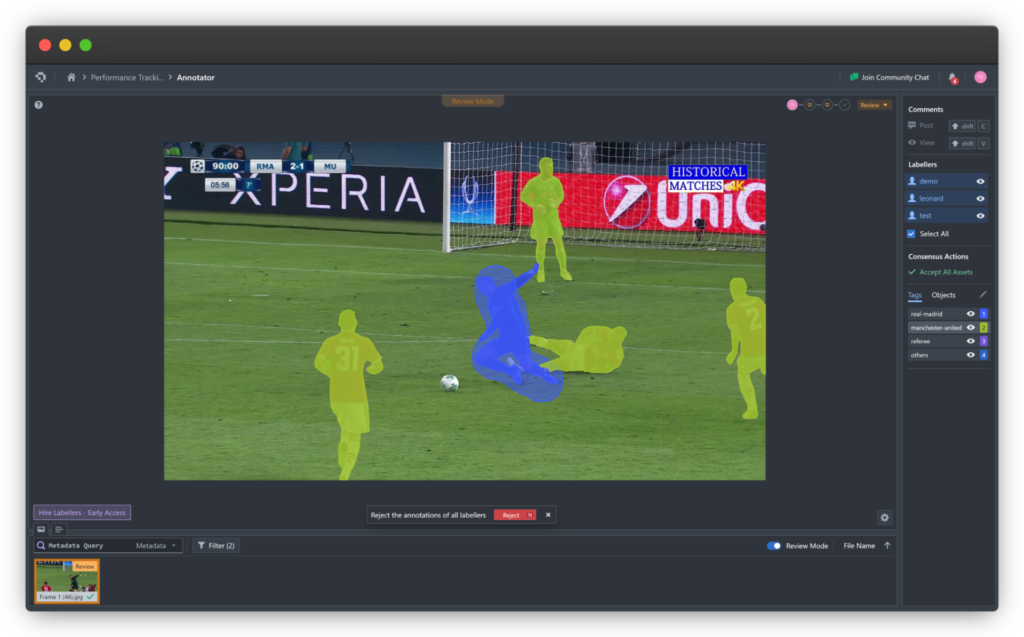
Pose estimation is a powerful Computer Vision technique designed to precisely track body movements in humans and animals. This article explores what pose estimation is, how it works, what techniques are used, and the wide range of applications it enables.
What is Pose Estimation?
Pose estimation refers to detecting and tracking the position and orientation of specific key elements – as human body parts – in an image or video.
For instance, if you have a photo of a person sitting, a pose estimation algorithm can analyze the image to locate their head, arms, and legs, as well as determine how those parts are positioned relative to each other.
Different methods are tailored for various needs:
- Human pose estimation is often used for activity recognition and body movement tracking.
- Head pose estimation focuses on determining head orientation.
- Animal pose estimation studies movement patterns across different species.
What is Human Pose Estimation?
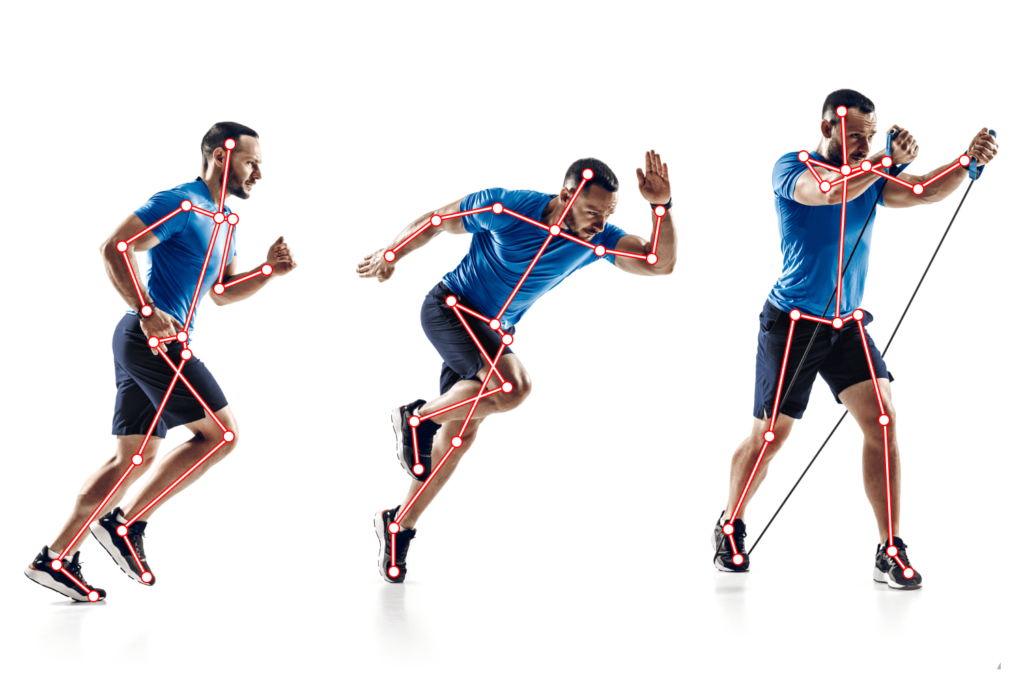

Human pose estimation is a Computer Vision task that identifies keypoints on the human body – such as the head, shoulders, elbows, and wrists – and connects them to form a skeletal structure. This allows the model to interpret and analyze body posture and movement accurately.
The process typically includes three steps:
- Input Processing
A machine learning model, usually based on a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), extracts visual features like edges, textures, and patterns from an image. - Keypoint Detection
The model produces heatmaps – one for each keypoint – representing the probability of a body part being at a specific pixel location. - Pose Construction
Detected keypoints are connected to form a skeletal structure. Techniques such as Part Affinity Fields (PAFs) are used to correctly associate body parts, even in complex or crowded images.
2D Human Pose Estimation
2D pose estimation identifies human body keypoints (e.g., joints) in a flat two-dimensional space—on an image or a single video frame. CNN-based models predict the coordinates of each joint and produce heatmaps representing their likelihoods.
This approach is fast and computationally efficient, making it suitable for tasks like walking or sitting detection. However, it struggles with depth perception and overlapping body parts, limiting its performance in complex poses.
3D Human Pose Estimation
3D pose estimation takes this further by reconstructing keypoints in three-dimensional space. Instead of simple pixel coordinates, it predicts (x, y, z) positions, offering a richer spatial understanding of body movements.
To achieve this, models may rely on camera calibration or depth sensors to capture accurate depth information.
While more detailed and useful for applications like motion capture or augmented reality, 3D estimation requires higher computational resources and is more sensitive to calibration errors.
Keypoint and Skeleton Detection
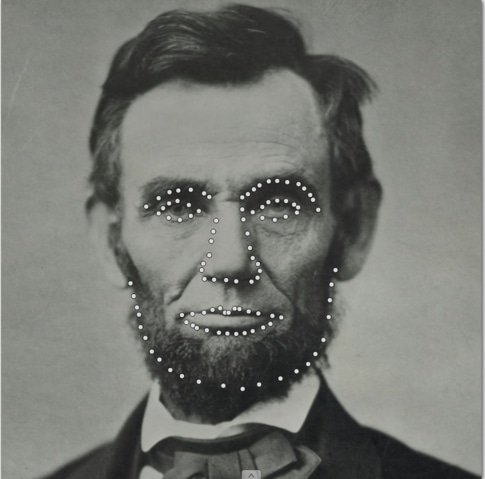

Keypoint Detection
This stage focuses on locating key joints—such as elbows, knees, and wrists—from an image or video. Each keypoint serves as a landmark, allowing the model to interpret body posture and structure. Accurate keypoint detection is essential for reliable pose estimation.
Skeleton Detection
After identifying keypoints, the system connects them to form a skeletal “stick-figure” model—linking the shoulder to the elbow, the hip to the knee, etc. This provides a visual and mathematical representation of the pose, enabling advanced movement tracking and posture analysis.
Deep Learning-based Pose Estimation Techniques
Modern pose estimation relies heavily on Deep Learning, particularly CNNs, to automatically learn spatial patterns. These methods generally fall into two main approaches:
- Top-Down Approach
The system first detects each person in the image, then performs pose estimation individually for each detected subject. It’s efficient and performs well under partial occlusions but can be less effective in crowded scenes. - Bottom-Up Approach
Here, the model first detects all keypoints in the image and then groups them into individual poses. It handles multiple people better but tends to be more computationally demanding.
Machine Learning Models for Pose Estimation
Several benchmark models have shaped modern pose estimation research and applications:
OpenPose
A pioneer in multi-person pose estimation.
- Uses a multi-stage CNN to detect and refine keypoints.
- Employs Part Affinity Fields (PAFs) to associate keypoints correctly, even in crowded scenes.
Its versatility makes it suitable for sports analytics, surveillance, and interactive media.
PoseNet
A lightweight, real-time model ideal for mobile or embedded devices.
- Built on MobileNet, optimized for speed without losing accuracy.
- Uses heatmap regression for joint localization.
It’s commonly applied in AR/VR systems and real-time gesture tracking.
AlphaPose
Designed for high-precision results, AlphaPose combines several innovations:
- Regional Multi-Person Pose Estimation (RMPE) for improved multi-person accuracy.
- Pose-Guided Proposal Generator (PGPG) for refined keypoint detection.
It’s widely used in animation, motion capture, and advanced human-computer interaction.
YOLOv7-Pose

An extension of the YOLO object detection family, optimized for real-time pose estimation.
It predicts human keypoints efficiently while maintaining YOLO’s signature speed, making it ideal for live video analysis where both object and pose detection are needed simultaneously.
MediaPipe Pose
Developed by Google, MediaPipe is an open-source framework that offers fast, real-time human pose tracking. It’s part of a broader suite supporting tasks such as face and hand detection.
Open Datasets for Pose Estimation
With the growing popularity of pose estimation, several datasets have been created to train and evaluate models:
- COCO Pose Dataset – Includes 17 keypoints for human body joints across varied real-world scenarios.
- MPII Human Pose Dataset – Contains over 25,000 annotated images from YouTube videos, focusing on everyday activities.
- Human3.6M – A large-scale dataset for 3D pose estimation with synchronized multi-camera and motion capture data.
- LSP (Leeds Sports Pose) – Features 10,000 sports-related images, ideal for 2D pose benchmarking.
Annotation for Pose Detection
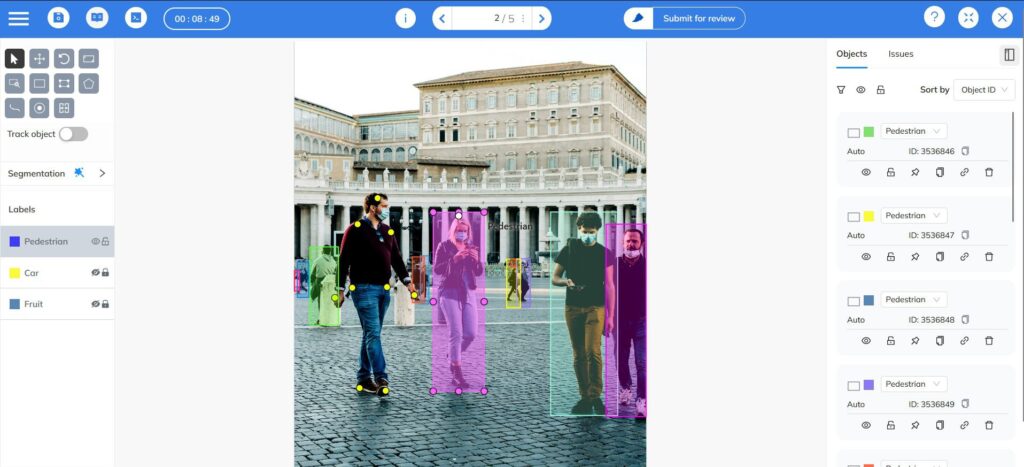
While open datasets are a strong starting point, custom applications often require tailored data.
A well-structured data pipeline is essential—beginning with collection and pre-processing, followed by data annotation, which is the most critical step.
For pose estimation, two key annotation techniques are used:
- Keypoint annotation – labeling specific joints or landmarks.
- Skeleton annotation – connecting keypoints to represent body structure.
Consistency and quality control are vital to ensure reliable training data.
Coral Mountain’s annotation platform, for example, provides an advanced keypoint labeling tool with integrated quality assurance options such as multi-annotator workflows and automated validation checks—helping teams maintain precise and consistent datasets.
Use Cases for Pose Estimation Applications
Healthcare
Used for patient monitoring, physiotherapy, and rehabilitation by tracking body movement patterns and progress.
Sports Analytics
Helps coaches and analysts understand athlete performance, technique, and potential risk of injury.
Robotics
Enables robots to interpret human gestures, improving collaboration and safety in industrial and service environments.
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI)
Facilitates gesture-based control in gaming, fitness, and VR/AR, enhancing immersion and accessibility.
Entertainment and Media
Applied in film and game production for motion capture, creating realistic digital characters.
Surveillance and Security
Improves threat detection and crowd behavior analysis through precise motion recognition.
Retail and Marketing
Powers virtual fitting rooms and shopper movement analysis, optimizing customer experience and store design.
In summary, pose estimation stands at the intersection of AI, Computer Vision, and real-world applications—transforming industries from healthcare to entertainment. With reliable datasets, precise annotation tools like those from Coral Mountain, and powerful deep learning models, understanding and recreating human motion has never been more accurate or accessible.
Coral Mountain Data is a data annotation and data collection company that provides high-quality data annotation services for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models, ensuring reliable input datasets. Our annotation solutions include LiDAR point cloud data, enhancing the performance of AI and ML models. Coral Mountain Data provide high-quality data about coral reefs including sounds of coral reefs, marine life, waves….
Recommended for you
- News
Most remote work today faces the same underlying economic pressure: commoditization driven by automation and global...
- News
Explore how AVs learn to see: Key labeling techniques, QA workflows, and tools that ensure safe...
- News
How multi-annotator validation improves label accuracy, reduces bias, and helps build reliable AI training datasets at...
Coral Mountain Data
Office
- Group 3, Cua Lap, Duong To, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam
- (+84) 39 652 6078
- info@coralmountaindata.com
Data Factory
- An Thoi, Phu Quoc, Vietnam
- Vung Bau, Phu Quoc, Vietnam

Copyright © 2024 Coral Mountain Data. All rights reserved.