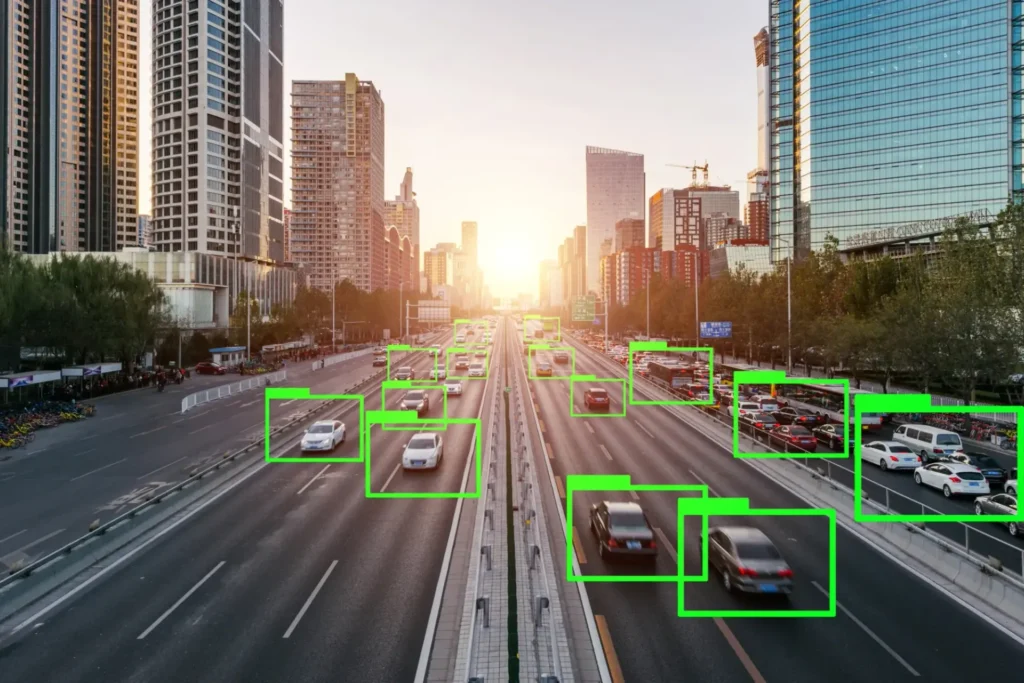
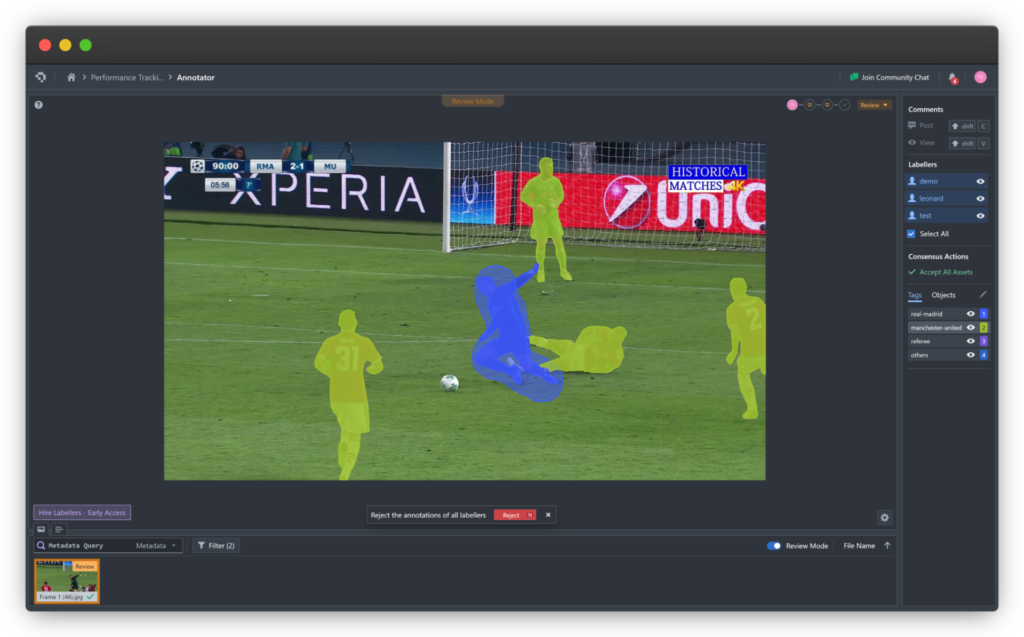
Learn everything you need to know about polyline annotations – what they are, where they’re used, and the benefits they offer.
Polyline annotation is one of the most widely used techniques in computer vision and machine learning, especially when it comes to interpreting elongated or continuous structures within visual data. This guide breaks down the fundamentals of polyline annotation, the AI models used to detect such structures, and the diverse real-world applications powered by this technology.

What is Polyline Annotation?
Polyline annotation involves plotting a sequence of connected points to form a line—or multiple lines—over an image. These traced paths are used to highlight linear patterns such as roads, field boundaries, pipelines, edges, and medical structures. Each plotted point acts as a control node, while the lines joining them capture the direction, curvature, and contour of the object being labeled.
Core advantages of polyline annotation include:
- Precision – Enables pixel-level accuracy when mapping elongated patterns.
- Adaptability – Easily handles curved or irregular structures.
- Functional depth – Serves as a foundational tool for mapping, segmentation, and tracking tasks.
Machine Learning models for detecting polylines in Images
Automatically detecting polylines in visual data requires specialized deep learning architectures capable of recognizing patterns that span across multiple pixels or frames.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
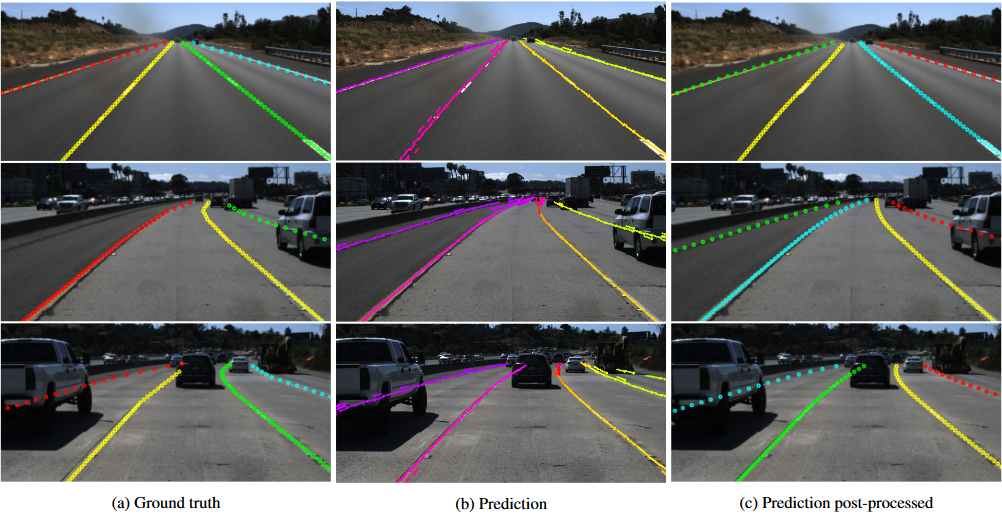
CNN-based models are frequently used for edge and boundary detection. Architectures such as YOLO and Mask R-CNN can be adapted to identify linear elements. A notable example is YOLinO (Generic Single Shot Polyline Detection in Real Time), which demonstrates high-speed lane and line extraction.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
RNNs—especially LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) networks—can model continuity, making them valuable when interpreting long, connected structures across spatial sequences.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs contribute by producing synthetic training examples that resemble real-world polyline patterns. This is particularly useful when labeled datasets are limited or expensive to generate manually.
Transformer Models
Attention-based architectures such as Transformers allow models to selectively focus on high-relevance regions in an image. Emerging models like PolyRoad leverage transformer-based mechanisms to more accurately detect lane boundaries and road edges.
Polyline detection use cases
Polyline annotation is widely applied across many industries. Below are some of its most impactful applications.
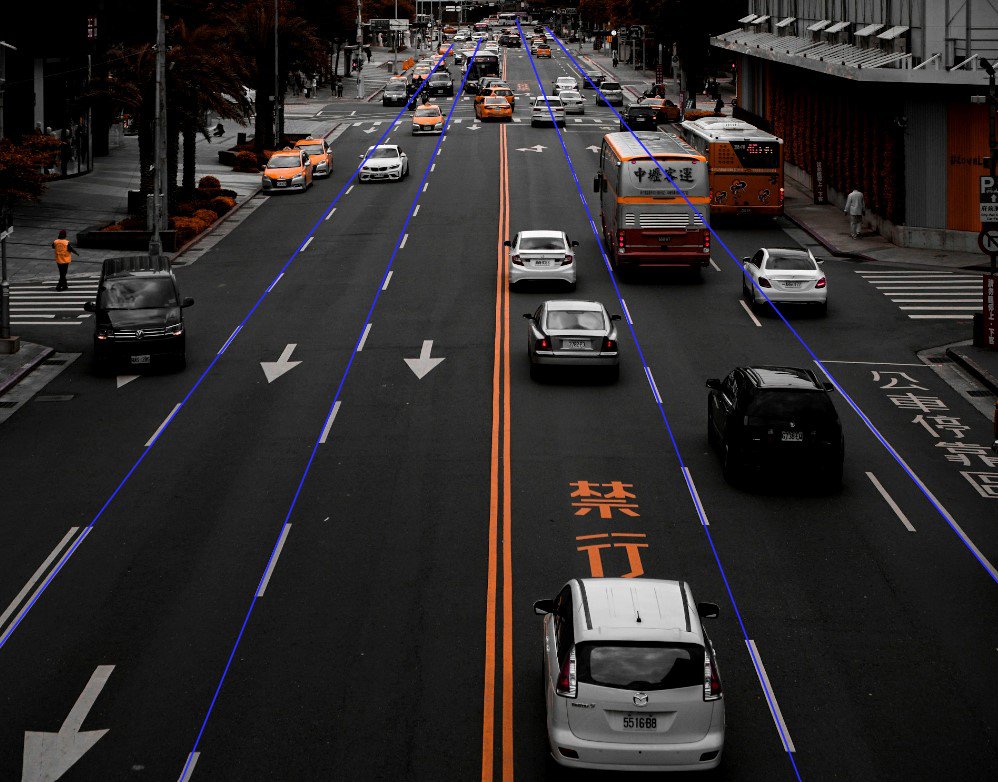
Autonomous Driving
- Lane Detection: Used to trace and track road lanes, forming the basis of ADAS Level 2 driving assistance.
- HD Road Mapping: Helps construct high-definition navigation maps with accurate markings and boundaries.
Geospatial Mapping
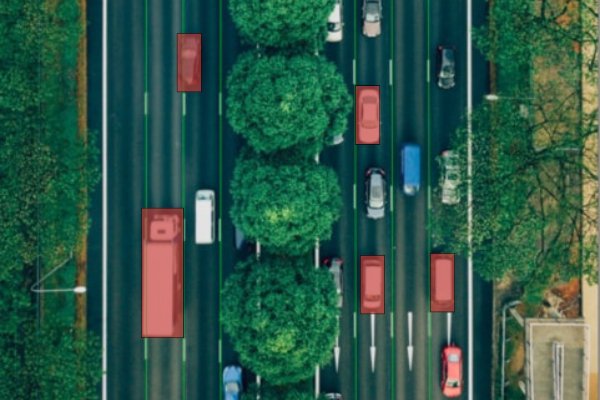

- Cartographic Tracing: Drawing rivers, borders, and utility layouts on topographic and aerial maps.
- Satellite Pipeline Detection: Identifying infrastructure such as railways and transmission lines.
Medical Imaging
- Blood Vessel Segmentation: Mapping vessels and neural pathways from MRI or CT scans.
- Pre-Surgical Planning: Highlighting critical anatomical paths ahead of minimally invasive procedures.
Agriculture
- Field Limit Delineation: Automatically outlining farm plot boundaries for monitoring.
- Irrigation Layout Planning: Labeling drainage and water channels for optimal distribution.
Urban Planning
- Infrastructure Drafting: Visualizing planned or existing road networks and power layouts.
- Traffic Flow Monitoring: Policymakers can analyze vehicular behavior by tracing intersections and crossings.
Environmental Monitoring
- Deforestation Analysis: Identifying advancing or retreating forest lines.
- Coastal Erosion Tracking: Detecting shifts in shoreline boundaries over time.
Robotics
- Path Planning: Robots use traced polylines as trajectories to follow.
- Object Alignment: Annotated edges help robotic arms grasp or cut precisely.
Challenges in Polyline Annotation
Despite its versatility, polyline annotation presents several hurdles:
- High Manual Effort: Creating accurate annotations at scale can be slow without automation.
- Consistency Management: Small labeling errors can mislead training models significantly.
- Complex Structures: Curved or branching shapes require nuanced tracing strategies.
- Data Sensitivity: In fields like healthcare, annotation must comply with strict privacy rules.
Conclusion
Polyline annotation is a critical asset in modern computer vision pipelines. From self-driving vehicles to medical diagnostics and environmental research, it acts as a bridge between raw imagery and actionable spatial understanding. As annotation platforms evolve and AI-assisted labeling improves, the precision and scalability of polyline-based systems will continue to expand—unlocking even more sophisticated perception capabilities.
Coral Mountain Data is a data annotation and data collection company that provides high-quality data annotation services for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models, ensuring reliable input datasets. Our annotation solutions include LiDAR point cloud data, enhancing the performance of AI and ML models. Coral Mountain Data provide high-quality data about coral reefs including sounds of coral reefs, marine life, waves….
Recommended for you
- News
Most remote work today faces the same underlying economic pressure: commoditization driven by automation and global...
- News
Explore how AVs learn to see: Key labeling techniques, QA workflows, and tools that ensure safe...
- News
How multi-annotator validation improves label accuracy, reduces bias, and helps build reliable AI training datasets at...
Coral Mountain Data
Office
- Group 3, Cua Lap, Duong To, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam
- (+84) 39 652 6078
- info@coralmountaindata.com
Data Factory
- An Thoi, Phu Quoc, Vietnam
- Vung Bau, Phu Quoc, Vietnam

Copyright © 2024 Coral Mountain Data. All rights reserved.